The ICR life sciences team has been conducting a large-scale comparison project of human versus chimp DNA sequence, the first phase of which has now been completed. The research involved the use of 40,000 purportedly random chimpanzee DNA sequences obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology that were produced as part of the chimpanzee genome project.1, 2 The sequences, on average, were 740 nucleotides each and were compared to four different versions of the human genome that were each ~3 billion bases. The DNA sequences were compared using a commonly employed algorithm called BLASTN.1
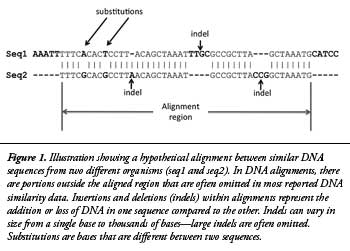 The BLASTN algorithm works by finding initial DNA base matches for the query sequence (chimp) compared to a target database (human) of a certain pre-specified length called “word sizes.”3 These initial matches are then extended outward in both directions until the matches are no longer statistically significant for similarity based on a pre-specified level of mathematical stringency called an “e-value” (or the query sequence ends). The end result of each successful query is called an alignment, often referred to as a database “hit.” Common default values used for BLASTN alignments include a word size of 11 and an e-value of 10. In this study, 15 different experiments testing combinations of three different word sizes (7, 11, and 15) and five different e-values (1,000, 10, 0.1, 0.001, and 0.00001) were performed. A simplified illustration of a hypothetical DNA alignment between two DNA sequences is shown in Figure 1.
The BLASTN algorithm works by finding initial DNA base matches for the query sequence (chimp) compared to a target database (human) of a certain pre-specified length called “word sizes.”3 These initial matches are then extended outward in both directions until the matches are no longer statistically significant for similarity based on a pre-specified level of mathematical stringency called an “e-value” (or the query sequence ends). The end result of each successful query is called an alignment, often referred to as a database “hit.” Common default values used for BLASTN alignments include a word size of 11 and an e-value of 10. In this study, 15 different experiments testing combinations of three different word sizes (7, 11, and 15) and five different e-values (1,000, 10, 0.1, 0.001, and 0.00001) were performed. A simplified illustration of a hypothetical DNA alignment between two DNA sequences is shown in Figure 1.
If present, the top alignment data (database hit) for each chimp query sequence were obtained. Depending on the e-value and word size combination, the average aligned region of each chimp sequence varied between 122 to 181 bases, 16 to 24 percent, respectively. Excluding data for the large amount of chimp sequence that failed to align, a very conservative estimate of human-chimp DNA similarity genome-wide is 86.4 to 88.9 percent, based on the initial round of research data. It is noteworthy that the parameters that produced the longest and more statistically robust alignments also produced the lowest similarities. Obviously, if the non-aligning chimp data were included in the final data summary, estimated similarities would be even lower.
The initial phase of this study was conducted with 600,000 attempted alignments under conditions that allowed for the comparison of all DNA sequence in both the chimp and human data sets. However, it may surprise people to know that when evolutionists compare DNA sequences, they employ something called low-complexity sequence masking, a feature that is thought to remove abundant DNA sequences that are less complex than those commonly associated with protein-coding regions. The masking (electronic removal) of these sequences in the comparison process speeds up the algorithm significantly.
Therefore, the second phase of these experiments is being conducted using the same algorithm parameters (word size and e-value combinations), with the addition of low complexity sequence masking to more accurately represent conditions that an evolutionist would use. A report on this second round of experiments, along with a complete summary of the entire study, will be provided in an upcoming issue of Acts & Facts.
References
- More information is available at blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- The Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium. 2005. Initial sequence of the chimpanzee genome and comparison with the human genome. Nature. 437 (7055): 69-87.
- Altschul , S. F. et al. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 215 (3): 403-410.
* Dr. Tomkins is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and received his Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University.
Cite this article: Tomkins, J. 2011. First Phase Complete in Human and Chimp Genome-Wide DNA Comparison. Acts & Facts. 40 (12): 6.