Many evolutionists theorize that dinosaurs evolved into modern birds. But to accomplish this, evolution would have had to overcome huge hurdles—such as the total reconstruction of certain skeletal, lung, and air-pumping mechanisms—because the way birds breathe is strikingly different in almost every respect to the respiration of reptiles.
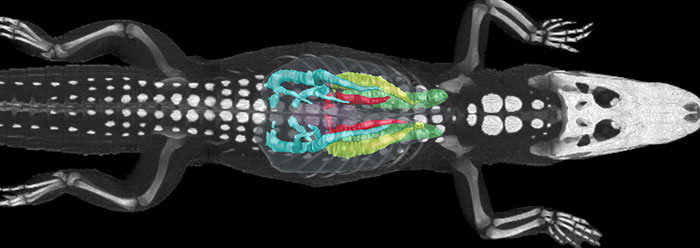
However, a new study has discovered that alligator lungs have more in common with the birds’ system of breathing than was previously suspected.1 Does this finding support the idea that birds evolved from dinosaurs?
The kinds of reptiles that evolutionists think "gave rise" to birds had bellows-style lungs and a diaphragm muscle to pump air. In stark contrast, birds breathe using one-way-airflow lungs suspended by a specially jointed skeleton and an interconnected series of air sacs. The birds' breathing apparatus takes up much more body space than the respiratory system of reptiles, and simultaneously contributes to birds’ light weight and streamlined shape.
Researchers C. G. Farmer and Kent Sanders from the University of Utah performed three different tests to measure airflow direction in alligator lungs. They found that air flows in one direction in certain chambers, and they called this “a strikingly birdlike pattern.”1
They cited prior studies which had evidently presumed that unidirectional airflow was completely dependent on the overall bird body plan. These new results have shown that one-way, flow-through channels do exist in lungs within the alligator’s anatomical setup. However, the study’s authors admitted that “it is unknown how it is possible to have unidirectional flow without air sacs and with diaphragmatic breathing.”1 They speculated that the flow is maintained by specialized loops and valves within the alligator lung.
These authors wisely did not interpret this finding as evidence that birds evolved from dinosaurs. Air sacs are part of an irreducibly complex bird breathing apparatus, which may also be interdependent with other features―like hollow bones, flight feathers, and wings―to enable bird flight. If one of these features were to be removed or significantly altered (which would have been inevitable during a bird’s evolution from any non-bird), the resulting malformed features would have resulted in malformed creatures.
A recent review of bird anatomy in comparison with that inferred for theropod dinosaurs, which some believe to be the evolutionary ancestors of modern birds, specified three core features in birds: (1) mechanisms that support outward and downward expansion and contraction of its ribcage, (2) an abdominal area large enough to accommodate sizeable and balanced air sacs, and (3) “specialized abdominal skeletal mechanisms,” like hinged rib bones, that ensure the air sacs will not collapse.2
Unidirectional airflow through lungs was not one of these core features. Therefore, the problem of how evolution could have built up these basic avian breathing characteristics incrementally remains unsolved.
Farmer said in a university press release, “The real importance of this air-flow discovery in gators is it may explain the turnover in fauna between the Permian and the Triassic.”3 Based on her results, she proposed an alternate evolutionary story wherein some of the most primitive reptile-like ancestors already had unidirectional airflow lungs, and their descendants variously evolved dinosaur, modern bird, or modern reptile body/lung designs.
The plasticity of evolutionary scenarios reveals more about human imagination than it does about the observed data. The unidirectional flow aspect of an alligator’s lung design appears fully integrated into its particular overall breathing apparatus, which is in turn well integrated into the alligator’s mode of living. In short, birds and alligators look as though they were separately and uniquely engineered.
References
- Farmer, C. G. and K. Sanders. 2010. Unidirectional Airflow in the Lungs of Alligators. Science. 327 (5963): 338-340.
- Quick, D. E. and J. A. Ruben. 2009. Cardio-Pulmonary Anatomy in Theropod Dinosaurs: Implications from Extant Archosaurs. Journal of Morphology. 270 (10): 1232-1246.
- Gators Breathe Like Birds. University of Utah press release, January 14, 2010.
Image credit: C. G. Farmer & Kent Sanders
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research
Article posted on January 28, 2010.