The Universe Was Created Recently
Many clock-like processes operating in the solar system and beyond indicate that the universe is young. For example, spiral galaxies should not exist if they are billions of years old. The stars near their centers rotate around the galactic cores faster than stars at the perimeters. If a cosmology based on long ages is correct, they should have blended into disk-shaped galaxies by now.
Comets pose a similar problem. They lose material each time they pass around the sun. Why would they still exist after vast eons? Saturn’s rings still look new and shiny. And many planets and moons are very geologically active. Surely the energy they continually expend should have been spent long ago if they are as old as they are usually claimed to be.
Instead, the more astronomers learn about the heavens, the more evidence there is that the universe is young.
Evidence for Creation › Evidence from Science › Evidence from the Physical Sciences › The Universe Was Created» Up One Level
Related Articles
Instrument data from the Cassini space probe have convinced planetary scientists that Saturn’s rings can be no more than a few hundred million years old.
[abstract_edit] =>
Instrument data from the Cassini space probe have convinced planetary scientists that Saturn’s rings can be no more than a few hundred million years old.
[stage] =>[stage_edit] =>
[body] =>
Data obtained by an instrument aboard the Cassini space probe have convinced planetary scientists that Saturn’s rings can be no more than a few hundred million years old.1 These new data confirmed some researchers’ previous suspicions. For instance, a previous ICR news article described how numerous planetary features within our solar system—including Saturn’s brilliant rings—look “young,” even to secular scientists.2
Numerous planetary features within our solar system—including Saturn’s brilliant rings—look “young,” even to secular scientists.
One of these features is the cleanness of Saturn’s rings. Secular scientists claim that the solar system is around 4.5 billion years old, so if Saturn’s rings were indeed that old, then they should have experienced billions of years’ worth of bombardment by micrometeorites. This would have blackened the icy ring particles, giving them a dark and sooty appearance.
The data obtained from Cassini’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA) allowed planetary scientists to measure the rate of micrometeorite bombardment:
The flux [of micrometeorite dust], about 10 times higher than estimates from before the Cassini mission, suggest a ring age of between 150 million and 300 million years, or even younger. “Our measurement is the most direct way you can measure it,” [space physicist Sascha] Kempf adds. “There’s not much you can do about it. It has to be young.”1
Note that the rings could be “even younger” than 150 million years. Could the rings be as young as 6,000 years, as implied by the Bible’s historical data? Of course they could, since the 150-300 million year estimate is an upper limit on the age of the rings.
Could Saturn's rings be as young as 6,000 years, as implied by the Bible’s historical data? Of course they could!
Since secular scientists have been forced to concede that the rings are young, they must somehow explain how the rings could have been formed in the relatively recent past, something which is extremely difficult. As noted by Jeff Cuzzi, an expert on Saturn’s rings, “Part of the reluctance for everyone to leap off this bridge into the unknown is we haven’t had any kind of feasible explanation [for how the rings could form recently].”1 Right now, secular scientists can only offer speculative, hand-waving explanations like these:
It was then that some sort of catastrophe befell the gas giant [Saturn]. Perhaps a stray comet or asteroid struck an icy moon, tossing its remnants into orbit. Or maybe the orbits of Saturn’s moons somehow shifted, and the resulting gravitational tug-of-war pulled a moon apart.1 (emphasis added)
As a systems administrator and a team leader on the Cassini project, creation scientist David Coppedge was able to occasionally interact with planetary scientists at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). He recounts,
It was clear to me that nothing would dislodge their belief in billions of years, but there was a subtext that it would be very troubling to them if the rings turned out to be young. These quotes [from reference 1] show that to be the case: they are flummoxed and dumbfounded by the evidence. They have no explanation, and they admit it.3
It should be noted in passing that Coppedge was demoted and eventually fired from his position at JPL in an appalling example of “viewpoint discrimination.” Coppedge’s “crimes” were that he privately shared “intelligent design” materials with his colleagues, and that he supported California’s Proposition 8 opposing homosexual marriage.4,5 Although Coppedge was apparently punished for sharing his own personal views, he recounts that his co-workers were allowed to freely express their personal beliefs with impunity.5 In spite of this blatant double standard, Coppedge lost his anti-discrimination lawsuit against JPL; the judge ruled against him without explanation.6
In spite of this injustice, Coppedge played a part in helping make the Cassini project possible, and the result is still more data confirming the youthfulness of our solar system.
References
- Voosen, P. Saturn’s rings are solar system newcomers. Science. 358 (6370): 1513-1514.
- Hebert, J. Youthful Solar System Bodies Puzzle Evolutionary Scientists. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org February 13, 2013, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Coppedge, D. F. It's Official: Saturn's Rings Are Young. Creation Evolution Headlines. Posted on crev.info January 3, 2018, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Klinghoffer, D. NASA Versus David Coppedge: Most Reprehensible Case of Anti-Intelligent Design Persecution Yet? Evolution News and Science Today. Posted on evolutionnews.org December 19, 2016, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Coppedge, D. F. Wheel of Fortune: The Liberal Culture of Shunning. Footprints of David Coppedge. Posted on davidcoppedge.com October 11, 2017, accessed January 4, 2018.
- Lee, S. After a fiery trial. World Magazine. Posted on wng.org May 28, 2016, accessed January 4, 2018.
*Jake Hebert is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in physics from the University of Texas at Dallas.
Stage Image Credit: Copyright © 2017. NASA. Used in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holder.
Article posted on January 8, 2018.
[body_edit] =>Data obtained by an instrument aboard the Cassini space probe have convinced planetary scientists that Saturn’s rings can be no more than a few hundred million years old.1 These new data confirmed some researchers’ previous suspicions. For instance, a previous ICR news article described how numerous planetary features within our solar system—including Saturn’s brilliant rings—look “young,” even to secular scientists.2
Numerous planetary features within our solar system—including Saturn’s brilliant rings—look “young,” even to secular scientists.
One of these features is the cleanness of Saturn’s rings. Secular scientists claim that the solar system is around 4.5 billion years old, so if Saturn’s rings were indeed that old, then they should have experienced billions of years’ worth of bombardment by micrometeorites. This would have blackened the icy ring particles, giving them a dark and sooty appearance.
The data obtained from Cassini’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA) allowed planetary scientists to measure the rate of micrometeorite bombardment:
The flux [of micrometeorite dust], about 10 times higher than estimates from before the Cassini mission, suggest a ring age of between 150 million and 300 million years, or even younger. “Our measurement is the most direct way you can measure it,” [space physicist Sascha] Kempf adds. “There’s not much you can do about it. It has to be young.”1
Note that the rings could be “even younger” than 150 million years. Could the rings be as young as 6,000 years, as implied by the Bible’s historical data? Of course they could, since the 150-300 million year estimate is an upper limit on the age of the rings.
Could Saturn's rings be as young as 6,000 years, as implied by the Bible’s historical data? Of course they could!
Since secular scientists have been forced to concede that the rings are young, they must somehow explain how the rings could have been formed in the relatively recent past, something which is extremely difficult. As noted by Jeff Cuzzi, an expert on Saturn’s rings, “Part of the reluctance for everyone to leap off this bridge into the unknown is we haven’t had any kind of feasible explanation [for how the rings could form recently].”1 Right now, secular scientists can only offer speculative, hand-waving explanations like these:
It was then that some sort of catastrophe befell the gas giant [Saturn]. Perhaps a stray comet or asteroid struck an icy moon, tossing its remnants into orbit. Or maybe the orbits of Saturn’s moons somehow shifted, and the resulting gravitational tug-of-war pulled a moon apart.1 (emphasis added)
As a systems administrator and a team leader on the Cassini project, creation scientist David Coppedge was able to occasionally interact with planetary scientists at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). He recounts,
It was clear to me that nothing would dislodge their belief in billions of years, but there was a subtext that it would be very troubling to them if the rings turned out to be young. These quotes [from reference 1] show that to be the case: they are flummoxed and dumbfounded by the evidence. They have no explanation, and they admit it.3
It should be noted in passing that Coppedge was demoted and eventually fired from his position at JPL in an appalling example of “viewpoint discrimination.” Coppedge’s “crimes” were that he privately shared “intelligent design” materials with his colleagues, and that he supported California’s Proposition 8 opposing homosexual marriage.4,5 Although Coppedge was apparently punished for sharing his own personal views, he recounts that his co-workers were allowed to freely express their personal beliefs with impunity.5 In spite of this blatant double standard, Coppedge lost his anti-discrimination lawsuit against JPL; the judge ruled against him without explanation.6
In spite of this injustice, Coppedge played a part in helping make the Cassini project possible, and the result is still more data confirming the youthfulness of our solar system.
References
- Voosen, P. Saturn’s rings are solar system newcomers. Science. 358 (6370): 1513-1514.
- Hebert, J. Youthful Solar System Bodies Puzzle Evolutionary Scientists. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org February 13, 2013, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Coppedge, D. F. It's Official: Saturn's Rings Are Young. Creation Evolution Headlines. Posted on crev.info January 3, 2018, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Klinghoffer, D. NASA Versus David Coppedge: Most Reprehensible Case of Anti-Intelligent Design Persecution Yet? Evolution News and Science Today. Posted on evolutionnews.org December 19, 2016, accessed January 3, 2018.
- Coppedge, D. F. Wheel of Fortune: The Liberal Culture of Shunning. Footprints of David Coppedge. Posted on davidcoppedge.com October 11, 2017, accessed January 4, 2018.
- Lee, S. After a fiery trial. World Magazine. Posted on wng.org May 28, 2016, accessed January 4, 2018.
*Jake Hebert is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in physics from the University of Texas at Dallas.
Stage Image Credit: Copyright © 2017. NASA. Used in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holder.
Article posted on January 8, 2018.
[typeID] => 9 [visible] => t [pdf] => [publishURL] => secular-scientists-dumbfounded-by-saturns [publishDate] => 0000-00-00 [authorAsterisk] => t [domainID] => 1 [publication] => [volume] => [issue] => [page] => [author] => Jake Hebert, Ph.D. ) -->
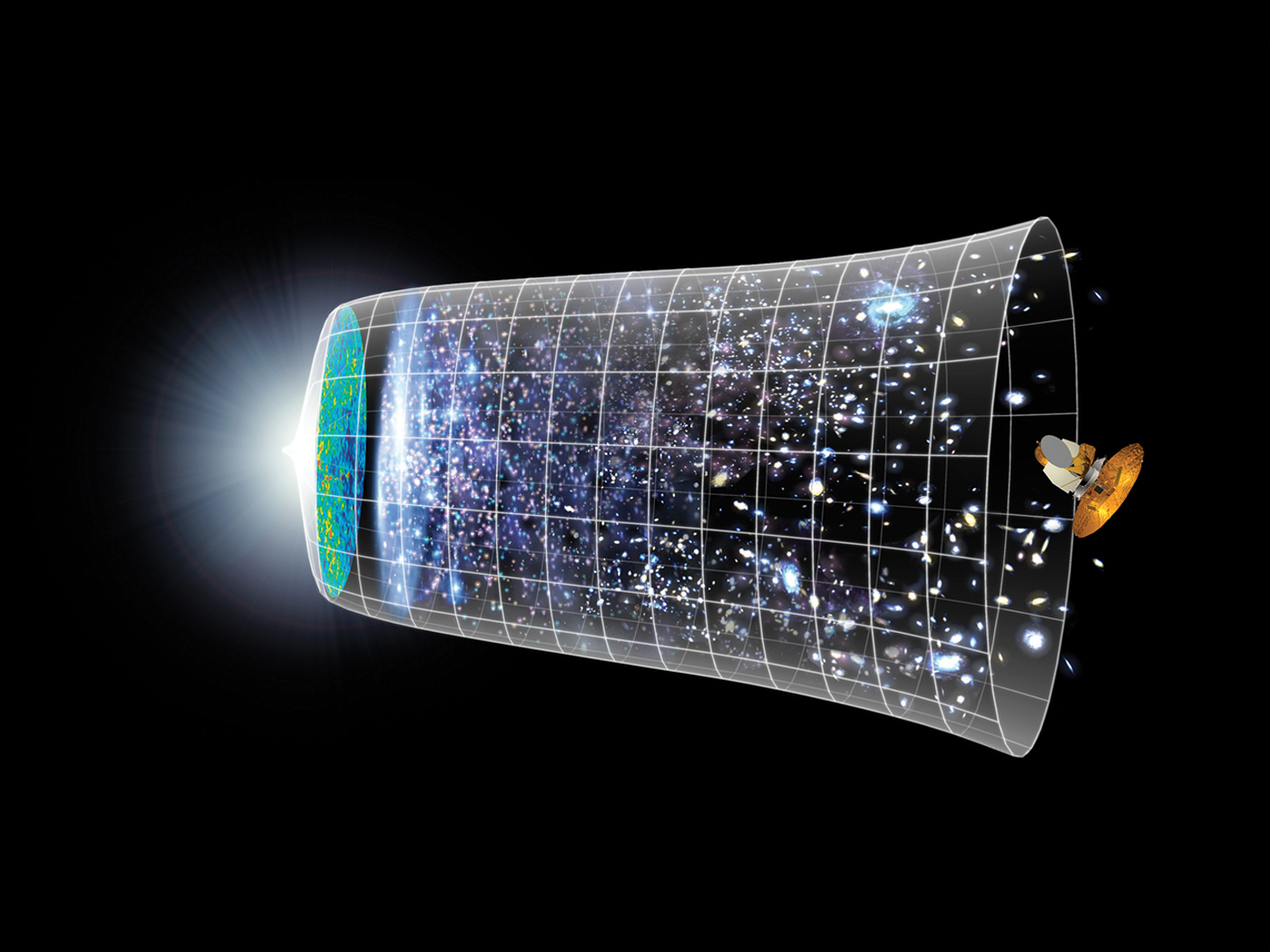
No doubt you've noticed the recent flurry of newspaper articles and TV interviews which have been proclaiming that the Big Bang theory had finally been proved. An observation by the COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer) satellite had verified a basic prediction of the Big Bang, so astronomers claimed. In fact, this discovery was so stupendous, "It was like looking at God, if you're religious," one said.
Within a week of the pronouncement, I happened to be at a major observatory, and discussed the find with a resident astronomer. He, too, was bubbling with excitement as he spoke. The Big Bang was now a fact, not merely a theory, I was told.
Upon further questioning, he admitted that the Big Bang concept had been at death's door, despite the fact that students have always been taught it, without reservation. This discovery had "saved" the Big Bang.
This astronomer admitted that many recent discoveries had seriously weakened the Big Bang theory. You see, the theory predicts some 15 or so billion years ago, all the matter and all the energy in the entire universe was packed into a single "cosmic egg," a super-dense electron-sized particle. An instability arose, and it exploded (i.e., in a big bang), producing an even distribution of matter and energy in all directions.
This was "proven" by the discovery, in 1964, of a very low-level background radiation the leftover "whisper" of the Big Bang. In all directions, the background radiation was measured at 2.7° Kelvin (equivalent to -270.5° Celsius!) with no variation—perfectly smooth.
But recent observations of the universe have revealed a very "lumpy" universe, with huge clusters of millions of galaxies and immense voids—not at all as expected from theory or the smooth background radiation. This led astronomers to propose that there must have been irregularities in the original "bang" to account for the present "lumpy" universe.
So now you know why astronomers were ecstatic when the COBE satellite measured small fluctuations in the background radiation, for now the Big Bang—everybody's favorite story—had been fully "proved."
But wait! It must be recognized that the variation has not been verified yet by others. No one has yet carefully examined the data. Most telling, the variation was extremely slight—only 30 millionths of a degree. At a lecture this week, one of the designers of the satellite told Dr. Gish that the COBE was not capable of measuring such a small variation. Others have said it is impossible for anything to be perfectly smooth, and even with these variations, the background radiation is smooth! And given the large-scale "lumpiness" or non-homogeneity of the universe, these small variations hardly seem related.
The astronomer I talked to said he was "quite religious, in a way." He knew there must be a God, since there were many things in astronomy he couldn't understand. But now he knew that God either must either be the Big Bang or have caused the Big Bang.
No, the Big Bang hasn't been "saved." At best, its death has been postponed for a few years. Worse, astronomers now have an excuse to continue in their "willful ignorance" (II Peter 3:3) and unbelief.
*Dr. John Morris is the President of ICR.
[body_edit] =>
No doubt you've noticed the recent flurry of newspaper articles and TV interviews which have been proclaiming that the Big Bang theory had finally been proved. An observation by the COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer) satellite had verified a basic prediction of the Big Bang, so astronomers claimed. In fact, this discovery was so stupendous, "It was like looking at God, if you're religious," one said.
Within a week of the pronouncement, I happened to be at a major observatory, and discussed the find with a resident astronomer. He, too, was bubbling with excitement as he spoke. The Big Bang was now a fact, not merely a theory, I was told.
Upon further questioning, he admitted that the Big Bang concept had been at death's door, despite the fact that students have always been taught it, without reservation. This discovery had "saved" the Big Bang.
This astronomer admitted that many recent discoveries had seriously weakened the Big Bang theory. You see, the theory predicts some 15 or so billion years ago, all the matter and all the energy in the entire universe was packed into a single "cosmic egg," a super-dense electron-sized particle. An instability arose, and it exploded (i.e., in a big bang), producing an even distribution of matter and energy in all directions.
This was "proven" by the discovery, in 1964, of a very low-level background radiation the leftover "whisper" of the Big Bang. In all directions, the background radiation was measured at 2.7° Kelvin (equivalent to -270.5° Celsius!) with no variation—perfectly smooth.
But recent observations of the universe have revealed a very "lumpy" universe, with huge clusters of millions of galaxies and immense voids—not at all as expected from theory or the smooth background radiation. This led astronomers to propose that there must have been irregularities in the original "bang" to account for the present "lumpy" universe.
So now you know why astronomers were ecstatic when the COBE satellite measured small fluctuations in the background radiation, for now the Big Bang—everybody's favorite story—had been fully "proved."
But wait! It must be recognized that the variation has not been verified yet by others. No one has yet carefully examined the data. Most telling, the variation was extremely slight—only 30 millionths of a degree. At a lecture this week, one of the designers of the satellite told Dr. Gish that the COBE was not capable of measuring such a small variation. Others have said it is impossible for anything to be perfectly smooth, and even with these variations, the background radiation is smooth! And given the large-scale "lumpiness" or non-homogeneity of the universe, these small variations hardly seem related.
The astronomer I talked to said he was "quite religious, in a way." He knew there must be a God, since there were many things in astronomy he couldn't understand. But now he knew that God either must either be the Big Bang or have caused the Big Bang.
No, the Big Bang hasn't been "saved." At best, its death has been postponed for a few years. Worse, astronomers now have an excuse to continue in their "willful ignorance" (II Peter 3:3) and unbelief.
*Dr. John Morris is the President of ICR.
[typeID] => 3 [visible] => t [pdf] => [publishURL] => has-big-bang-been-saved [publishDate] => 0000-00-00 [authorAsterisk] => f [domainID] => 1 [publication] => [volume] => [issue] => [page] => [author] => John D. Morris, Ph.D. ) -->