Okay, I admit most folks have probably not thought to ask this creation question. But a bigger question gets answered when we examine the fantastic butterfly features that counter the force of falling raindrops.
Okay, I admit most folks have probably not thought to ask this creation question. But a bigger question gets answered when we examine the fantastic butterfly features that counter the force of falling raindrops.
Butterfly wings are quite thin. How do these tiny creatures cope with raindrops that land at 22 miles per hour? Cornell scientist Sunghwan Jung led a project that tested water drop impacts at real raindrop speeds.1 It turns out that special surface structures on butterfly wings manage the drop impacts, which Professor Jung compared to the force of bowling balls falling from the sky on humans!2
How do these special surfaces manage killer raindrops?
At the level seen only with a microscope, we find the wings covered in rough bumps. If a drop hits flat on a sheet of glass, its force spreads in a widening wave. But when a raindrop hits a butterfly wing, the tiny bumps rupture that spreading force so that one big drop shatters into dozens of tiny droplets.
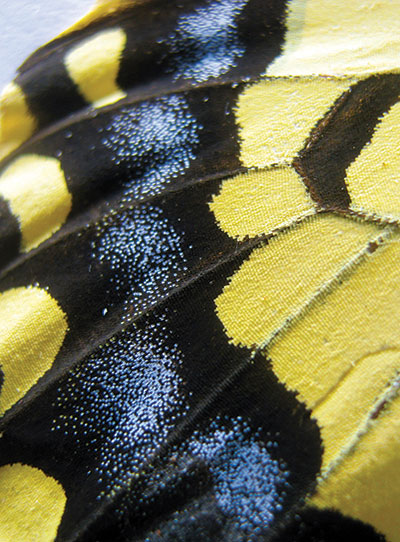 Zoom in even closer to nanoscopic levels and we find wax structures that make the wings water-resistant. The droplets bounce right off. Without them, water would stay on the wings longer, and that would wick too much heat from tiny insect bodies. The research team found that this ingenious, thin surface cuts the water contact time by 70%.1 The wings stay dry and whole, and the tiny flying animals stay warm and airborne.
Zoom in even closer to nanoscopic levels and we find wax structures that make the wings water-resistant. The droplets bounce right off. Without them, water would stay on the wings longer, and that would wick too much heat from tiny insect bodies. The research team found that this ingenious, thin surface cuts the water contact time by 70%.1 The wings stay dry and whole, and the tiny flying animals stay warm and airborne.
So, these scientists found the answer to our question: Butterfly wings resist raindrop power using clever micro-bumps and nano-waxes. The researchers also discovered these structures on dragonfly and moth wings, plant leaves, and even bird feathers.
That leads us to the bigger question: If these amazing features help keep these creatures alive and in flight, how did such structures arise?
Many scientists attribute creature designs to random changes guided by natural factors over eons. But whoever crafted these super-surfaces must have done it with flight in mind right from the start. These surfaces combine with the lightweight but strong materials and structures, navigation systems, functional landing gear, and aerodynamic shapes that all work together to make a butterfly flutter. Nature knows nothing, let alone the precise placement of parts required for flight. Truly the Lord Jesus, not natural processes, deserves all the credit for rainproofing butterfly wings before the first rain fell.
References
- Kim, S. et al. 2020. How a raindrop gets shattered on biological surfaces. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (25): 13901-13907.
- Ramanujan, K. Armor on butterfly wings protects against heavy rain. Cornell Chronicle. Posted on cornell.edu on June 8, 2020, accessed June 15, 2020.
* Dr. Thomas is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool.