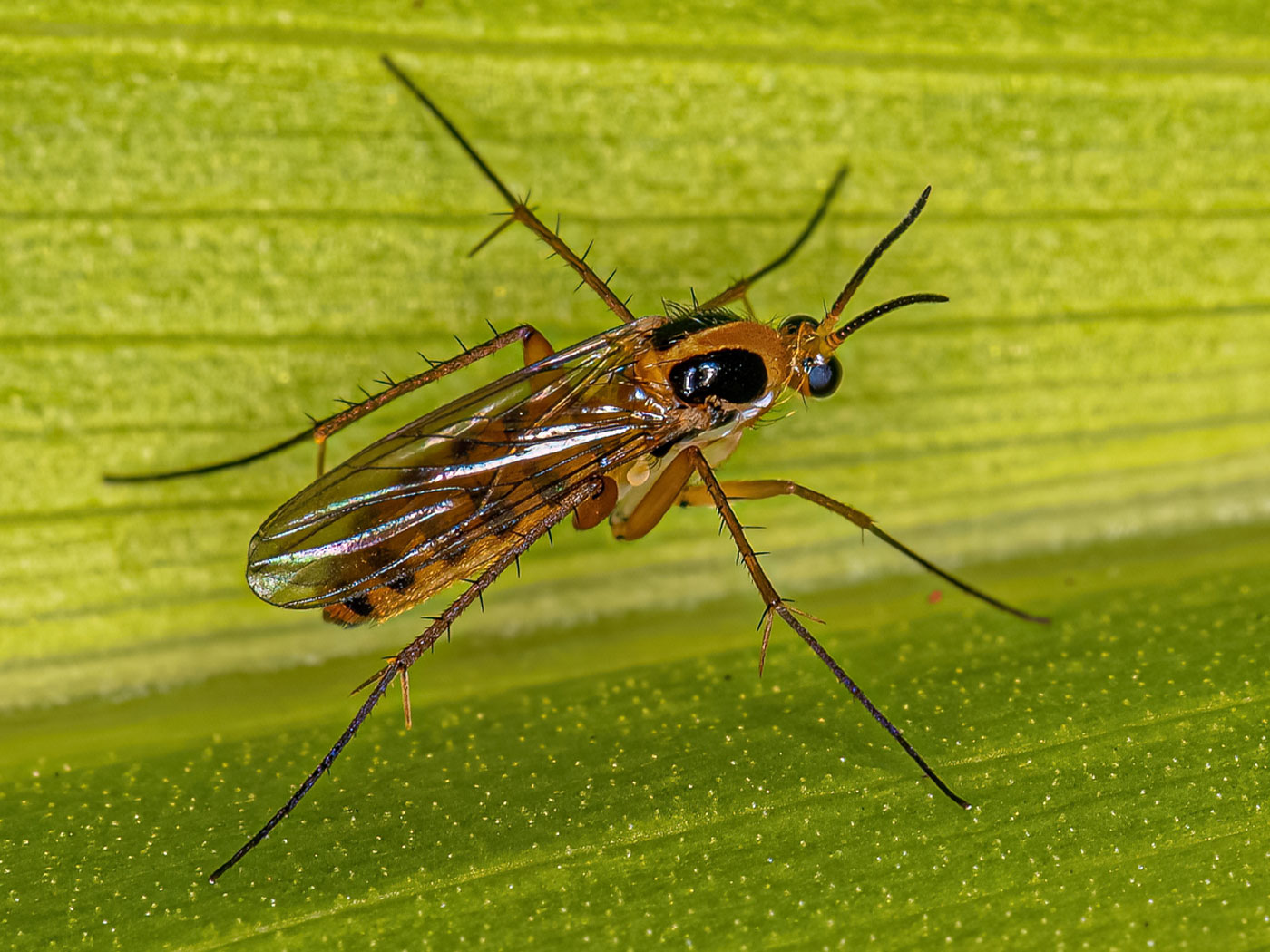
If ancient history according to Scripture is true, then what should we expect to find in animal fossils? Surely excellent body designs would top the list, closely followed by a lack of "transitional forms." A newly discovered specialized beetle inside Indian amber provides another peek into the past and an opportunity to test these Bible-based expectations.
Joseph Parker, a research associate at the American Museum of Natural History, specializes in this type of ant beetle, called Protoclaviger. He told the AMNH, "Protoclaviger is a truly transitional fossil."1 He and AMNH curator David Grimaldi coauthored a paper describing the find in Current Biology, where they wrote, "Protoclaviger captures a transitional stage in the evolutionary development of this novel body plan, most evident in its still-distinct abdominal tergites."2
Tergites are the segments of an insect's body, and the several hundred modern species of Protoclaviger do not have them. Instead, modern varieties have smooth, solid bodies. Is that all it takes to make a bona fide evolutionary transition? After all, the genetic basis for this kind of difference may be quite small, and the basic body form of this beetle looks the same as a modern variety.3 The fossil form is so similar to today's ant-loving beetles, classified in the family Clavigeritae, that it was easy to identify.
Entomologists are still unravelling the elaborate tactics these beetles use to live inside ant colonies, where they somehow convince worker ants to feed them directly, but the AMNH press release described a few of the known tactics. Ant-loving beetles actually have specialized mouth parts designed to receive liquid food from worker ants. They have special glands that secrete "oily secretions" all over their bodies.1 Tufts of hair-like projections called trichomes wick secretions outward, and ants in the colony constantly sample these secretion-soaked trichomes. Two of these trichomes stand out, like backward-pointing horns, with just the right size to fit ant mouths.
The fossil beetle has these same trichomes, too. The AMNH admitted that "its body is very similar to modern Clavigeritae beetles," but then noted that Protoclaviger still has tergites on its abdomen and so it must be a transitional form.4
But transitional forms are supposed to have clear transitional features, like an otherwise ant-beetle body but without its trichomes, which had not yet evolved. What's transitional about sectioned beetle abdomens versus smooth ones? Instead, both the modern and fossilized versions of this beetle share the shapes, size, and unique features befitting its life in an ant colony.
This fossil, easily recognized as an ant-loving beetle, has everything it needed to live among ancient ants. Protoclaviger is a great example of a well-designed body one would expect from animals that God created, and it also exemplifies fossils that look too similar to known living kinds to illustrate evolutionary transitions.
References
- Snyder, K. 52-Million-Year-Old Amber Preserves "Ant-Loving" Beetle. American Museum of Natural History press release. Posted October 2, 2014, accessed December 4, 2014.
- Parker, J., and D. Grimaldi. Specialized Myrmecophily at the Ecological Dawn of Modern Ants. Current Biology. 24 (20): 2428-2434.
- While a small change to most genes does not produce a difference in body shape, a small change in certain critical genes like the Hox gene can produce dramatic effects to insect bodies.
- The full quote including context reads, "Although its body is very similar to modern Clavigeritae beetles, with two stark, hook-like trichomes, some of its characteristics are clearly more primitive. For example, Protoclaviger's abdominal segments are still distinct, whereas in modern beetles they are fused together into a single shieldlike segment."
*Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on December 18, 2014.