Longtime followers of ICR should be familiar with our research into original organics in fossils. Over 100 peer-reviewed secular publications have shown that one might discover original tissue remnants in fossils from any region.1 Still-soft organics hail from almost every continent.2 Could organics still exist in fossils near ICR’s Dallas offices, where summer sunlight regularly bakes the earth with triple-digit heat?
Longtime followers of ICR should be familiar with our research into original organics in fossils. Over 100 peer-reviewed secular publications have shown that one might discover original tissue remnants in fossils from any region.1 Still-soft organics hail from almost every continent.2 Could organics still exist in fossils near ICR’s Dallas offices, where summer sunlight regularly bakes the earth with triple-digit heat?
ICR’s new research cooperation with an award-winning microscopist has focused on fossils from West Texas. No original organics would remain after one million years, especially in the Texas heat since high temperatures accelerate biochemical breakdown.3 If original organics occur in the fossils from these rocks, then they will look younger than ever.
One technique that targets the protein collagen in bone is called cross polarized light microscopy (XPOL). Research begins with preparing very thin sections of bone. A microscope fitted with crossed polarizers (“cross polars”) can detect regions in the sample where something twists the light. In bone, that something is collagen.
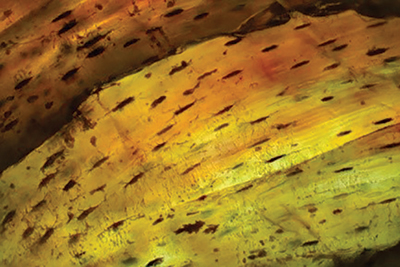
Fresh bone comes densely packed with collagen, which looks bright gold under cross polars. Bone with no collagen looks almost black—it shows no image.4 Between these extremes, ancient bone shows traces of collagen that twist wisps of light into the detector.
Sure enough, we looked at spectacular XPOL images in very old fossils that showed exactly what collagen traces should do to polarized light. Figure 1 shows fossil bone from an extinct alligator-size tetrapod named Diadectes collected from the famous red beds of West Texas. The small dark dots are lacunae that once held bone cells. Long streaks show the banded pattern of collagen in bone.
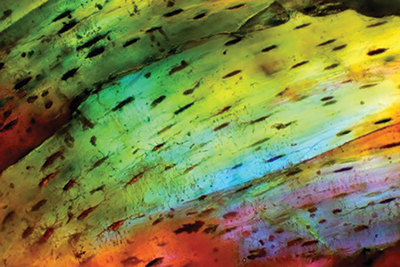
A first order retardation plate5 attachment enhances the presence of the light-bending agent found within this Permian bone, assigned a secular age of about 280 million years. Figure 2 shows the same spot as Figure 1 within the Diadectes bone but with the first order red plate that phase-shifts some of the gold light into other colors. As long as collagen remains embedded in the bone matrix, blues turn gold and vice versa while a microscopist rotates the sample. Watch the video at the top of this page to see light shifting through partly collagenated fossil bone.
XPOL light microscopy is just one more tool—alongside a few dozen others—that scientists use to help describe collagen in fossil bone. As with the other 100-plus soft tissue discoveries, these bones look thousands, not millions, of years old. A burial of these animals in Noah’s Flood among the vast red beds only thousands of years ago could account for the presence of collagen despite the Texas heat.
References
- List of Biomaterial Fossil Papers (maintained). Online document. Posted on docs.google.com, accessed November 8, 2020.
- Thomas, B. 2020. Soft Tissue Fossils Reveal Incriminating Trends. Acts & Facts. 49 (11): 9.
- Thomas, B. 2019. Collagen Decays Too Fast for Evolutionary Time. Acts & Facts. 48 (8): 9.
- Using two pairs of polarized sunglasses, align two lenses in front of your eyes with one swiveled 90 degrees from the other to demonstrate the light-extinguishing effect of cross polars.
- See the Introduction to the Compensators and Retardation Plates fact sheet. Olympus. Posted on olympus-lifescience.com.
* Dr. Thomas is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool.