In their quest to try and find some sort of evolutionary similarity between humans and apes, scientists have compared DNA, proteins, anatomy, behavior, and every other conceivable feature. But many of these attempts showed that a huge chasm of dissimilarity exists with no distinct evolutionary connection. And now, a new study comparing saliva between humans and apes is once again showing the uniqueness of humans and the failure of evolutionary reasoning.1
Your saliva is a highly designed and precise combination of important proteins required for preprocessing food in your mouth prior to entering your digestive tract. Human saliva also contains other specific types of proteins needed for the maintenance of tooth mineralization and protection from microbial pathogens. The sum total of the complement of proteins in saliva is called the salivary proteome.
In a recent research study, scientists compared the salivary proteomes of humans with two ape species considered to be our closest living evolutionary relatives: chimpanzees and gorillas. They also included monkeys (Rhesus macaque) as an evolutionary out-group—an alleged distant relative.
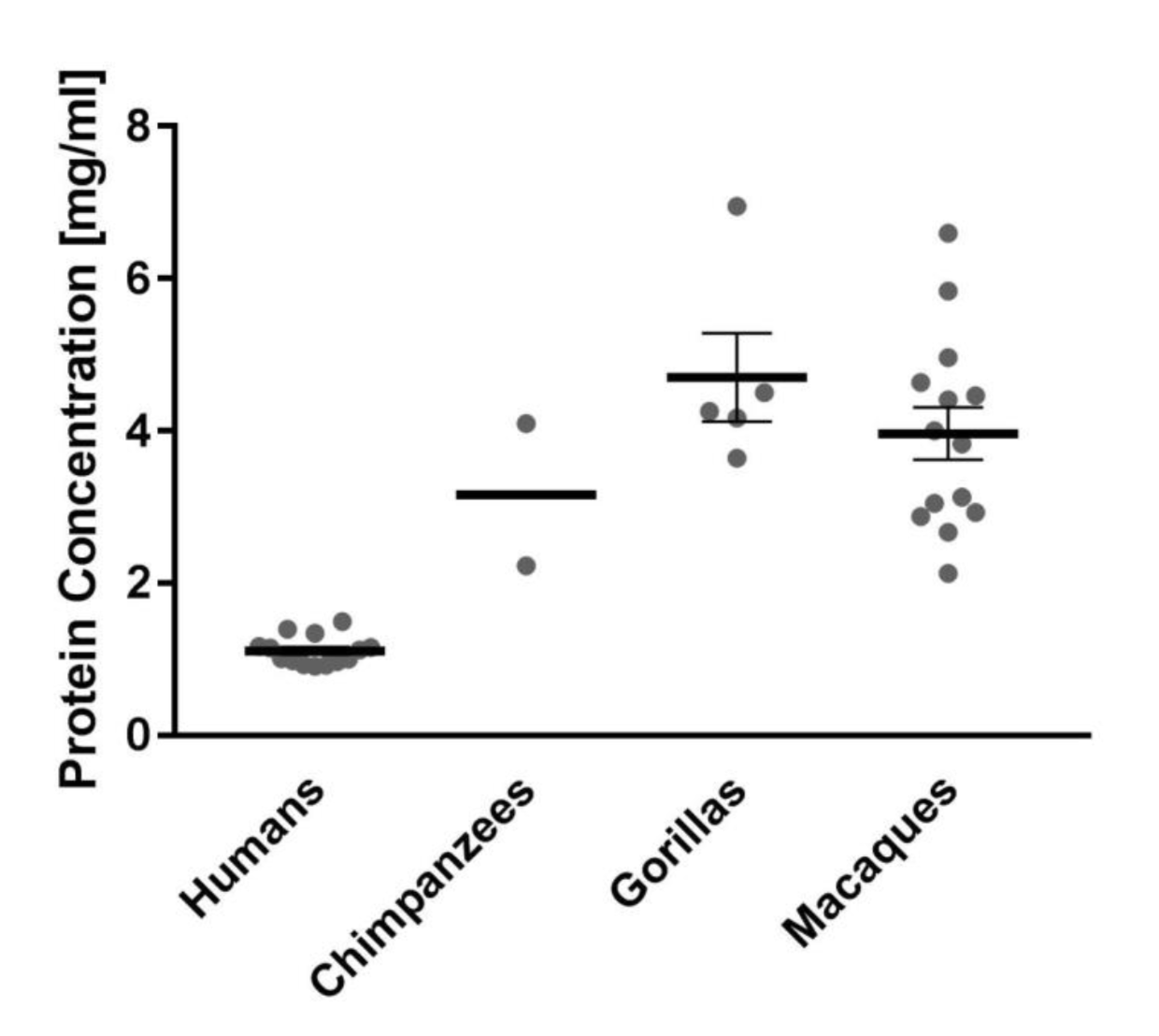
The first major difference the researchers noted was that human saliva is much more watery and diluted than apes’ and the overall concentration of proteins is much lower. In fact, human saliva contains half the total amount of proteins compared to apes and macaques (see figure).
The next thing the scientists observed was that the concentrations of the major groups of proteins is markedly different between humans and apes as well. The researchers also noted that human-specific proteins were found that do not exist in apes. Overall, the salivary proteomes were distinctly different between not just humans and apes, but also between chimps, gorillas, and macaques.
In their conclusion, the researchers stated, “We discovered unique protein profiles in saliva of humans that were distinct from those of nonhuman primates.” They also claimed, “Certain properties and components of human and nonhuman primate saliva might have evolved in a lineage-specific manner.”1 The term “lineage specific” means there is no evolutionary overlap; each human, ape, and monkey salivary proteome is unique.
This observance doesn’t line up with evolution, but fits well with Genesis that tells us God created each type of creature after its kind.2 Humans, chimps, gorillas, and macaques are unique kinds, and both science and scripture continue to confirm this biological truth.
References
1. Thamadilok, S. et al. 2020. Human and Nonhuman Primate Lineage-Specific Footprints in the Salivary Proteome. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 37 (2): 395-405.
2. Genesis 1:21, 25
Dr. Tomkins is Life Sciences Director at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his doctorate in genetics from Clemson University.
Ape Spit Radically Different from Human
The Latest
Biblical Giants in the News
Recent claims that an Egyptian papyrus scroll may affirm the past existence of giants have gone viral,1,2 and news outlets still reported...
March 2026 ICR Wallpaper
"Behold, I will do a new thing, Now it shall spring forth; Shall you not know it? I will even make a road in the wilderness And rivers in the desert." (Isaiah...
Creation Kids: Ladybugs
Hi, kids! We created a special Acts & Facts just for you! Have fun doing the activities while learning about the wonderful world God...
North Cascades National Park: Assembled During the Flood and...
North Cascades National Park is sometimes called “the American Alps” for its stunning vistas that average about 5,000 feet above sea level,...
Engineered Genomic Changes in Adaptation
Programmed genome rearrangements (PGRs) are deliberate, genetically controlled changes in an organism’s DNA sequence and chromosome structure...
How Can I Know Evolution Is Wrong?
Evolution pushes Christians to doubt what our Bibles say about creation by asserting impersonal processes made everything over eons. Scripture asserts...
What Is a Charitable Gift Annuity?
A charitable gift annuity (CGA) is a simple, proven way to make a gift to ICR and receive fixed income for life—often at rates higher than CDs....
ICR in Thailand
As the unified body of Christ, we marvel when individual notes come together to form beautiful harmonic chords. Dino Dave and Dr. Brian were blessed...
Making a TOBD Easy: A Conversation That Says It All
“I get what you’re saying! And I would love to think about biology from a design perspective, but I don’t even know where to begin,”...
Creation Research Debunking Chromosome 2 Fusion Confirmed by...
Recent conventional genetic research published in Cell Genomics undeniably confirms findings that were previously reported by the Institute for Creation...