Fruit flies have been the foundational invertebrate of biology research for decades. Not only do they resist change, but there’s no record—fossil or otherwise—of their evolution from an unknown arthropod ancestor and they are clearly not related to any other creature.1-3 They have always been fruit flies.
Researchers have recently discovered new miniscule fruit fly design features that point to the Creator. The finding involves insights into extremely small holes (nanopores) found on the sensilla (small sensory detectors in invertebrates) of the fruit fly’s body.4 The insect is able to detect—smell—biomolecules in the air through these nanopores. A nanometer is one millionth of a millimeter. Biologists have discovered that nanopores also form elaborate structures on the surface of other living things—from plants to vertebrates like peacocks.
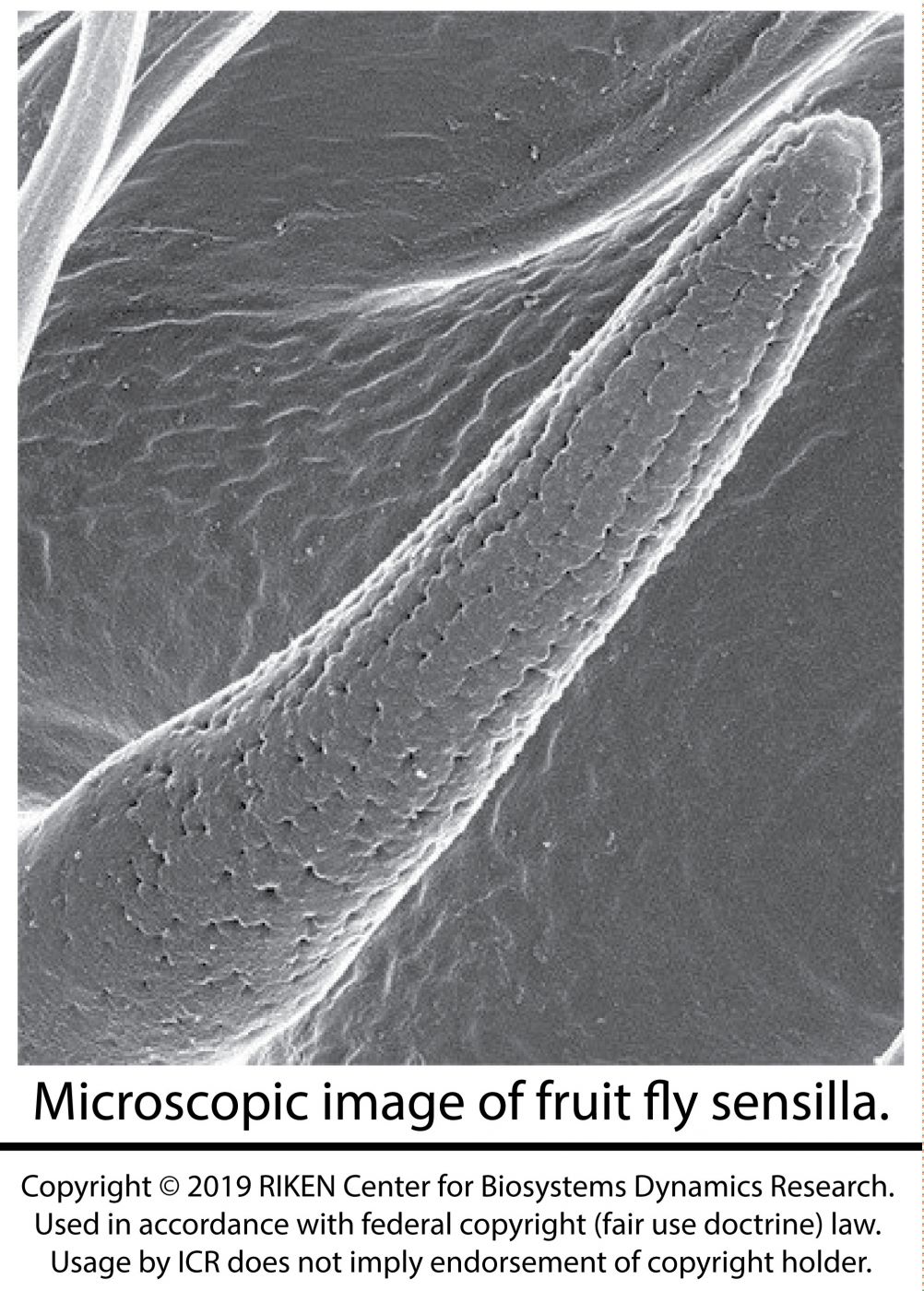 A collaboration of academic and private researchers in Japan recently identified an important gene responsible for the development of these nanopores.4 By using advanced microscopy and DNA analysis techniques, they isolated the gene and its pattern of expression, naming it gore-tex.
A collaboration of academic and private researchers in Japan recently identified an important gene responsible for the development of these nanopores.4 By using advanced microscopy and DNA analysis techniques, they isolated the gene and its pattern of expression, naming it gore-tex.This new gore-tex gene plays a key role in the formation of these tiny pores. They aren’t just holes, but living filters that allow the entrance of some molecules important in olfaction (the capacity to smell), but keep out bigger airborne particles. In fact, the nanopores themselves are just one part of an elaborate sensory system of signal detection and processing that involves many complex features that could only have arisen by an Omnipotent and All-Wise Creator. ICR scientist, Dr. Randy Guliuzza has been extensively documenting this important feature of adaptive engineering termed Continuous Environmental Tracking or CET.
The gore-tex gene is a member of Osiris—a large family of 24 different genes that are essential for development in insects. Osiris genes appear suddenly in insects with no evolutionary precursors. Not surprisingly, evolutionists state the Osiris genes are “highly conserved” or similar among insects.5 Creationists agree that common code performs similar functions in unrelated creatures, like different kinds of insects, but this doesn’t mean that a fruit fly can evolve into a grasshopper. Fruit flies have always been fruit flies and Osiris genes are part of a common code package for insects—a prediction of designed and engineered systems.
The insects as a general group never evolved, and the various created kinds of insects, like fruit flies, didn’t either. ![]()
The insects as a general group never evolved, and the various created kinds of insects, like fruit flies, didn’t either. They were created complete and fully-formed, right down to their unique genetic toolkits and nanopores.
References
1. Thomas, B. 2010. No Fruit Fly Evolution Even after 600 Generations. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org November 16, 2010.
2. Sherwin, F. 2006. Fruit Flies in the Face of Macroevolution. Acts & Facts. 35 (1).
3. Sherwin, F. 2019. Are People and Fruit Flies Related? Acts & Facts. 48 (2): 16.
4. Ando, T. et al., 2019. Nanopore Formation in the Cuticle of an Insect Olfactory Sensillum. Current Biology. 29: 1-9. doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.03.043.
5. Smith, C. et al. 2018. Conserved roles of Osiris genes in insect development, polymorphism and protection. Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 31 (4): 516-529.
*Mr. Frank Sherwin is Research Associate at ICR and received a master’s in zoology from the University of Northern Colorado. Dr. Jeffrey Tomkins is Director of Life Sciences at ICR and earned a Ph.D. in genetics from Clemson University.