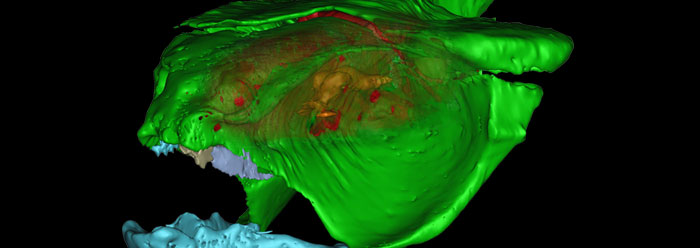
Scientists have accidently discovered a rare and perhaps unique fossilized brain of an iniopterygian, an extinct kind of ratfish or chimaera that supposedly lived 300 million years ago. When the researchers scanned the fossilized skull of the iniopterygian with advanced imaging techniques at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, nobody expected to see a brain.1 British naturalist Charles Darwin predicted that “no organism wholly soft can be preserved.”2 Yet here was fossilized soft tissue. How could this be?
One hypothesis is that the environment in which the fish died was very rich in certain compounds. The skull portion of the fossil is “almost pure calcium carbonate,” and the fossilized brain is mostly calcium phosphate. The researchers surmised that this difference arose from the acidity of the brain tissues, which were more attractive to the dissolved calcium phosphate than to the calcium carbonate from the surrounding environment. In addition, there must have been a “lack of oxygen,” because oxygen readily reacts with delicate soft tissues and quickly disintegrates them. However, this fossil brain did not disintegrate. The scanned images revealed specific brain features: “the cerebellum, spinal cords or optic lobes and tracts, among others.”3
Even with the lack of oxygen, how did calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate replace the bone and brain tissues? The chemicals, dissolved in water, were transported across gaps and pores in the fish. It is possible that the chemical content of the water could have changed rapidly during the time that the different parts of the fish were decaying. Such fast-moving and chemical content-changing water is consistent with cataclysmic flood models based on the biblical account of the Flood.
The fish would have been rapidly buried by a mineral-laden soup and covered with tons of overburden (material that severely warped this specimen and flattened most others within its rock stratum), perhaps within hours. The initial phases of the global Flood very likely sealed off the fish remains from atmospheric oxygen, helping to preserve the extremely soft brain tissues. A similar scenario would have also fossilized jellyfish, which are soft-bodied animals made of 96 percent water and which decay on the beach in mere hours. Darwin would undoubtedly be surprised to learn that such fossils have been discovered in Wisconsin and elsewhere.4
Since the Bible’s historical data is usually ignored in most scientific investigations, it comes as no surprise that this recent discovery “all happened by chance.”3 The researchers would not expect to find fossilized soft brain tissues if today’s slow processes were all that was at work in the past. However, given the catastrophic formation indicated by most of earth’s geologic structures and the massive extermination of life represented in the fossil record—as well as the preservation of soft tissue from creatures supposedly millions of years old—the biblical Flood is a valid and relevant interpretive key to earth’s past. It can be expected that more soft tissue fossils, including brains and perhaps visceral organs, will be found.
References
- Pradel, A. et al. 2009. Skull and brain of a 300-million-year-old chimaeroid fish revealed by synchrotron holotomography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Published online before print March 9, 2009.
- Darwin, C. R. 1859. The Origin of Species. Middlesex, England: Penguin Classics, 298.
- Scientists discover the first fossil brain. European Synchrotron Radiation Facility press release, March 3, 2009.
- Hagadorn, J. W., R. H. Dott, and D. Damrow. 2002. Stranded on a Late Cambrian shoreline: Medusae from central Wisconsin, Geology. 30 (2):147-150.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer.
Article posted on March 11, 2009.
Image Credit: P. Janvier