A recent poll of college-age Americans showed that the single most convincing science-based argument for evolution is the lineup of supposed ape-like evolutionary ancestors of mankind.1 But epidemic disagreement among researchers over the relevance and position of every thus-far-proposed human ancestor undermines confidence in this fluctuating and fragmented fossil lineup. Creation researcher Marvin Lubenow called it “the fake parade” in his book Bones of Contention.2 A new ape-fossil study adds even more reason to decry this fossil parade as a fake.
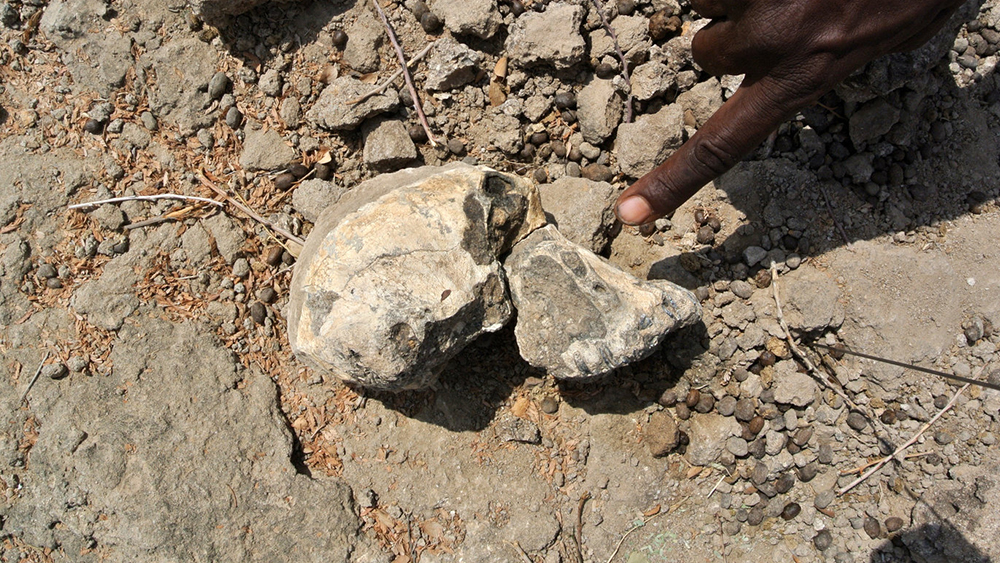
Publishing in the journal Nature, a team of experts described a fossil skull that puts both a new face and a contradictory age onto an extinct ape variety previously known only from teeth and bone fragments.3 The team discovered the fossil in 2016 in the Afar region of Ethiopia. Early on, they recognized it as an australopithecine ape, but after analysis, they assigned it to the species anamensis.
Australopithecus anamensis supposedly evolved into Australopithecus afarensis—the most famous example of which is nicknamed Lucy—which some have asserted became humans. But many evolutionists see no anatomical link between this extinct ape kind and mankind. One zoologist admitted, “They are just apes.”4
Bible-respecting scientists see both Australopith varieties as members of the same created ape kind—now extinct. From this perspective, they would have lived at the same time but perhaps in different places, much like the two chimp varieties on Earth today. The common chimp Pan troglodytes has a wide habitat range, whereas the more rare pygmy chimp (bonobo) Pan paniscus appears to only live south of the Congo River in the Congo Basin.
The story of supposedly ancestral A. anamensis evolving into A. afarensis was easier to tell back when A. anamensis fossils occurred in rock layers below, and thus before, those of A. afarensis. But this newly described A. anamensis skull received an evolutionary age that overlaps its supposed descendant by 100,000 years. Lead author of the Nature paper Haile-Selassie told the Max Planck Institute, “This is a game changer in our understanding of human evolution during the Pliocene.”5
Talk about an overstatement. Rather, this is a game-ender for merely the Australopith backstory of one of the many human evolution narratives. The long overlap in evolutionary time erases notions of an ancestor-descendant relationship between these extinct ape varieties, but leaves intact the Genesis-friendly model of variations within kinds.
References
1. Biddle, D. A., and J. Bergman. 2017. Strategically dismantling the evolutionary idea strongholds. Journal of Creation. 31(1): 116-119.
2. Lubenow, M. 2004. Bones of Contention. Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Books, 167.
3. Haile-Selassie, Y. et al. 2019. A 3.8-million-year-old hominin cranium from Woranso-Mille, Ethiopia. Nature. Posted on Nature.com before print, August 28, 2019, accessed September 2, 2019.
4. Lewin, R. 1987. Bones of Contention: Controversies in the Search for Human Origins. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 164.
5. A face for Lucy’s ancestor. Max Planck Institute. Posted on mpg.de August 28, 2019, accessed September 2, 2019.
Stage image: cranium of Australopithecus anamensis
Stage image credit: Copyright © Dale Omori, Cleveland Museum of Natural History. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
Dr. Thomas is a Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool.

Fossil Ape Skull Is a Game Ender
The Latest
New Titanosaur Species Discovered in Uruguay and Argentina
The pre-Flood world had some truly massive dinosaurs, and the largest of them were in the group Sauropodomorpha.1 Within this group were...
May 2024 ICR Wallpaper
"Have I not commanded you? Be strong and of good courage; do not be afraid, nor be dismayed, for the LORD your God is with you wherever you...
Was a Key to Photosynthesis Evolution Discovered?
Northern Canadian lakes were the source of recently discovered unique photosynthetic bacteria of the phylum Chloroflexota. After years of culturing,...
CREATION PODCAST
Four Moons That Indicate a Young Universe | The Creation Podcast:...
Earth has one moon, but Jupiter has many! What can we learn from our celestial neighbor's satellites? Do they indicate youth?
Host...
Creation Kids: Seeds and Sprouts
by Renée Dusseau and Susan Windsor*
You're never too young to be a creation scientist and explore our Creator's world. Kids, discover...
APOLOGETICS
Christ’s Creativity in Canyon Critters
Grand Canyon animals display many marvelous traits and behaviors as they live life in that harsh habitat. These canyon creatures succeed thanks to the...
Standing Against False Science
I’m Michael Stamp, and I’m in my 12th year as an editor at the Institute for Creation Research. It’s always an encouragement to see...
Oysters and Pre-Flood Longevity
The oyster species Crassostrea virginica, also known as the eastern oyster, is a prized seafood. Research has demonstrated that a fossil version of...
Galápagos Finches: A Case Study in Evolution or Adaptive Engineering?
A group of birds known as Darwin’s finches live in the Galápagos Islands, which are located in the Pacific Ocean 600 miles west of Ecuador....
Hot Springs National Park: Hydrothermal Springs Formed By The...
Hot Springs National Park is located about an hour southwest of Little Rock in the folded Ouachita Mountains of central Arkansas. It is the second smallest...