A recent news story featured a variety of science writers repeating the meme "Fish grow 'hands' in genetic experiment." These sensationalized stories attempted to describe a new genetics research study published in the journal Developmental Cell.1 The primary results of the study actually produced data that refuted the accompanying evolutionary hype.
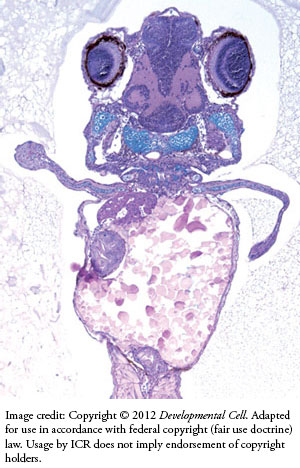 For starters, the genetically modified zebrafish embryos under investigation had no hands at all. When New Scientist magazine questioned one of the researchers, Fernando Casares, about the popularized claim, he responded, "Of course, we haven't been able to grow hands."2
For starters, the genetically modified zebrafish embryos under investigation had no hands at all. When New Scientist magazine questioned one of the researchers, Fernando Casares, about the popularized claim, he responded, "Of course, we haven't been able to grow hands."2
Nevertheless, Casares and his colleagues did claim that their data had profound implications for the hypothetical evolutionary change required for fish fins to magically morph into legs, arms, hands, and feet. This mythical process would have been necessary for fish to transition to land animals. And contrary to common evolutionary claims, this dogma is not supported by any actual transitional forms in the fossil record.3
The zebrafish has been an important model organism for the study of embryology, because it can be easily manipulated by modifying its DNA. Researchers can then observe the effects in developing embryos. These genetic manipulations can be easily observed in the transparent fish embryos, which provide a window into the developmental process.
In this study, scientists inserted a control element (genetic switch) from mouse DNA into some zebrafish. The switch drastically ramped up the expression of a key developmental zebrafish gene called hoxd13. This caused a manifold increase in the hoxd13 gene product in developing fish fin tissue.
So, what were the effects of over-expressing the hoxd13 gene? Not only did the fish not develop hands or any other novel evolutionary favorable appendage, but normal fish fin development was completely and grotesquely perturbed. The resulting embryos died within four days on average—hardly a hallmark of evolutionary progress.
The mutated results of the study was that the normal tissue area of expression for the hoxd13 gene was markedly expanded beyond its normal, well-defined boundaries. It produced grossly distorted and lengthened sections of perturbed tissue. In fact, the growth distortions were not symmetrical but exhibited uncontrolled development.
Evolutionary media were quick to propagate a story where fish supposedly grew hands in the lab. But the actual experimental results told just the opposite story. Altering only a single gene's expression level disrupted the finely tuned system of hundreds of interacting genes within the irreducibly complex developmental genetic network, resulting in death of the organism.
Rather than showing how limbs could be produced from fins, this research showed how wonderfully fine-tuned and built the genome is.
References
- Freitas, R. et al. 2012. Hoxd13 Contribution to the Evolution of Vertebrate Appendages. Developmental Cell. 23 (6): 1219-1229.
- Zebrafish made to grow pre-hands instead of fins. New Scientist. Posted on newscientist.com December 15, 2012, accessed December 26, 2012.
- See Chapters 8 and 9 in Morris, J. D. and F. J. Sherwin. 2010. The Fossil Record: Unearthing Nature's History of Life. Dallas, TX: Institute for Creation Research.
* Dr. Tomkins is a Research Associate and received his Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University.
Article posted on January 7, 2013.
























