After a ten-year-long flight, the European Space Agency's (ESA) Rosetta spacecraft entered into orbit around a comet. It will soon attempt to actually land a probe on the comet's surface. Though data-gathering has only just begun, the comet is already divulging secrets.
ESA's Director General Jean-Jacques Dordain told ESA, "Europe's Rosetta is now the first spacecraft in history to rendezvous with a comet, a major highlight in exploring our origins. Discoveries can start."1
But the list of discoveries that the ESA expects may be too lofty for a lowly comet. Space.com quoted Mark McCaughrean, a senior scientific adviser for ESA, as saying during an August 6 webcast, "The really big questions here are, 'Where do we come from? Where does the solar system we live in come from? How was it put together? How was it assembled? How did the planets get built up individually, and how did water get to this planet that we live on?'"2
ESA News said, "Comets are considered to be primitive building blocks of the Solar System and may have helped to 'seed' Earth with water, perhaps even the ingredients for life. But many fundamental questions about these enigmatic objects remain, and through a comprehensive in situ study of the comet, Rosetta aims to unlock the secrets within."1
Could the secrets of this comet's structure, composition and behavior really supply answers to such grand questions?
Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, named after its discoverers, already presents more questions than answers. As the Rosetta spacecraft approached the comet, it measured gas and dust near the comet for six weeks. "In the same period, first measurements from the Microwave Instrument for the Rosetta Orbiter, MIRO, suggested that the comet was emitting water vapour into space at about 300 millilitres per second," according to the ESA.1
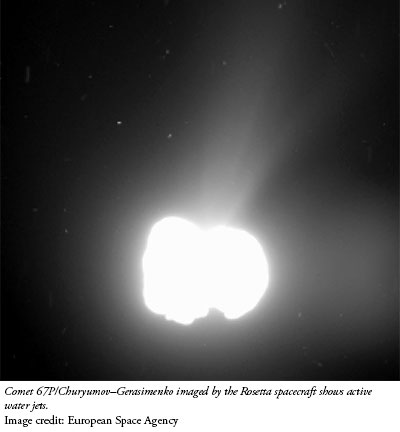 That's over six-thousand gallons per day! At that rate, the whole comet—assuming it's made entirely of water ice—would melt into space after only hundreds of thousands years. The dumbbell-shaped mass spans two and a half miles across its longest axis. If this comet was really a "primitive building block of the Solar System," then it's supposedly 4.5 billion years old. Why is it still around if it keeps getting smaller as it swings around the sun every six and a half years?
That's over six-thousand gallons per day! At that rate, the whole comet—assuming it's made entirely of water ice—would melt into space after only hundreds of thousands years. The dumbbell-shaped mass spans two and a half miles across its longest axis. If this comet was really a "primitive building block of the Solar System," then it's supposedly 4.5 billion years old. Why is it still around if it keeps getting smaller as it swings around the sun every six and a half years?
Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko's mass shrinks not only from water-vapor loss, but solar wind also blows away material as it orbits nearer the sun—between Earth and Mars when it's closest. If it's really billions of years old, why isn't this comet old, cold, and dead—why does it exist at all? Rosetta's investigation has not yet entered full swing, and already reveals the comet as looking young, warm, and alive.3
No wonder Matt Taylor, ESA's Rosetta project scientist said, "Our first clear views of the comet have given us plenty to think about."1
References
- Bauer, M. Rosetta Arrives at Comet Destination. European Space Agency. Posted on esa.int August 6, 2014, accessed August 6, 2014.
- Kramer, M. 5 Amazing Facts about Europe's Comet-Chasing Rosetta Probe. Space.com. Posted on space.com August 6, 2014, accessed August 6, 2014.
- The ESA article in reference 1 says, "Meanwhile, the Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer, VIRTIS, measured the comet's average temperature to be about –70ºC, indicating that the surface is predominantly dark and dusty rather than clean and icy." This temperature is warmer than the space around the comet at its current position, so these scientists suggest that dark dust absorbs enough light to raise the comet's temperature to 70 C.
Image credit: European Space Agency
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on August 13, 2014.