Introduction
For many decades biology students have been taught the unscientific doctrine that prokaryotic cells are "primitive" in spite of their obvious complexity.1 Creation scientists counter that if it's a living organism, it's necessarily complex. Only those steeped in Darwinian dogma continue to maintain microorganisms such as bacteria are simple.
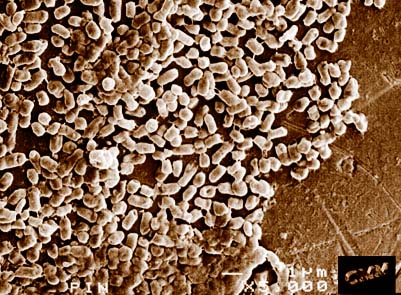
Photo of E. coli on a pinhead courtesy of: Rick Webb, Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, The University of Queensland.
Mycoplasmas: Unique Bacteria
The trillions of cells that make up people and animals do not have a cell wall but a plasma membrane. Plants and prokaryotes (which includes bacteria) possess a rigid cell wall composed of cellulose plus the critical plasma membrane. Mycoplasmas are a unique type of bacteria in that they do not have a cell wall. However, they can be just as pathogenic (disease-causing) as some "ordinary" bacteria, with one species causing walking pneumonia, or PAP.
In 1979, evolutionist Thomas Brock suggested that mycoplasmas were of "special evolutionary interest because of their extremely simple cell structure."2 But years later two authors stated, "Mycoplasmas can no longer be thought of as a simple organism."3 Notice that with more research, the "simple" mycoplasma turned out to be extremely complex.
Creation scientists said as much, but of course were ignored. The same complexity has been discovered within other bacterial species.
E. coli: Testament to Complexity
The 2000 edition of the prestigious Annual Review of Microbiology contains an intriguing article titled "Interim Report on Genomics of escherichia coli"4 that discusses the bewildering complexity of this oft-studied bacterium. The article is replete with phrases such as "regulation systems," "transport systems," and other complex cellular processes. E. coli is an important bacterial species normally found in the large intestine. It is one of the most thoroughly and intensely studied of all microorganisms and is found any place where there are people or animals. Occasionally, E. coli makes the headlines when foods are contaminated with uncommon pathogenic strains of this bacterium.
Evolutionists traditionally have viewed bacteria such as E. coli as simple forms of life. These single-celled organisms, so the story goes, were one of the first life forms to have sprung naturalistically from an unknown ancestor several billion years ago. Therefore they "must be" of a simple construction.
However, contrary to evolutionary assumptions, laboratory research has shown even simple bacteria to be enormously complex. Evolutionist James Shapiro of the University of Chicago states:
The past decade has also witnessed the discovery of new phenomena, such as autoaggregation of chemotactic bacteria and coordinated behaviors in complex colony morphogenesis. . . . bacterial cells have communication and decision-making capabilities that enable them to coordinate growth, movement, and biochemical activities.5
Are these not altogether amazing processes for a "simple" organism?
Just how "primitive" is E. coli? Biologists still are not sure. The authors of the article on E. coli in the Annual Review of Microbiology wrote:
Even though the entire sequence of the E. coli K-12 chromosomal DNA has been known for [over] two years, we are still far from knowing all of the details of how the cell operates, lives, replicates, coordinates, and adapts to changing circumstances . . . the number of experimental journal articles on aspects of the basic biology of E. coli has increased from an average of 78 per month in 1996 to an average of 94 per month today . . . new biological information about this well-studied organism continues to roll in. New metabolic capabilities are discovered and are connected to underlying genes. There are new regulation systems, new transport systems, and more information on cellular constituents and cellular processes.6
. . . but how many regulators are needed to maintain coordination of expression of the genes and correct interaction among the gene products? Regulation systems are not the same in all bacteria, and we still do not have all of the information for the regulatory networks of even one bacterial species . . . the minimal set of genes and proteins necessary for life of an independently replicating cell does not have an easy answer.7
Experimentation into details of the biology of E. coli continues unabated today, and the numbers of papers published annually continues to increase . . . not all enzymes and pathways in E. coli are known . . . besides genes for unknown enzymes, we have data for enzymes that don't have genes. There are 55 enzymes of E. coli that have been isolated, purified and characterized over the years, but their genes have never been identified.8
The advent of massive DNA-sequencing technology and the completion to date of [more than] 20 microbial genomes that are now available to the public have not brought us (yet) to a complete understanding of exactly how a single free-living cell functions and adapts to changing environments.9
Creation scientists cheerfully predict that, if, and when, science does have a complete understanding of how a free-living cell functions and adapts, evolutionism will have nothing to do with it.
Another bacterial species heretofore considered "simple" is Pseudomonas aeruginosa which causes infections in cystic fibrosis patients and burn victims, and hospital-acquired pneumonia in patients on respirators. Once again, however, the complexity of this "simple" bacterium (which allegedly is closely related to E. coli) is startling.
Consistent with its environmental versatility, P. aeruginosa has nearly 300 cytoplasmic membrane transport systems. . . . [it] appears to have the most complex chemosensory systems of all the complete bacterial genomes [total genetic makeup of an organism] . . . P. aeruginosa has broad capabilities to transport, metabolize and grow on organic substances, numerous iron-siderophore uptake systems and the enhanced ability to export compounds (for example, enzymes and antibiotics) . . .10
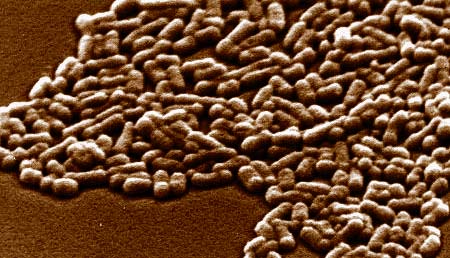
E. coli photo courtesy of: Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, The University of Queensland
Conclusion
Autoaggregation? Regulatory networks? Transport systems? Coordinated behavior? Communication and decision-making capabilities? Enhanced export abilities? Is this why we should believe simple bacteria evolved from non-living chemicals? One could just as easily be speaking of a massive, hi-tech automated factory—a sophisticated organization that certainly doesn't spring up by chance, time, and natural processes! This is yet one more example of how evolutionary theory is contrary to the facts of science.
Why do evolutionists insist on teaching that bacteria (prokaryotes) are simple or primitive when empirical research states the opposite? Worse, how can they say that "simple" life evolved from non-life using nothing but natural selection, chance and time?
As one creation biologist so clearly stated, when people make things smaller and smaller, it's considered a wonder of modern technology (nanotechnology). When "nature" does it, it's primitive.
References
- Clark, D.P., Russell, L.D. Molecular Biology, Cache River Press, 1997.
- Brock, T.D. Biology of Microorganisms, 3rd ed., Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1979 p. 723.
- Dybvig, K., Voelker, L.L. "Mycoplasmal molecular biology," Annual Review of Microbiology, 1996, p. 48.
- Riley, M., Serres, M.H., "Interim report on genomics of Escherichia coli" Annual Review of Microbiology, 2000 pp. 341-411.
- Shapiro, J.A., "Thinking about bacterial populations as multicellular organisms" Annual Review of Microbiology, 1998, pp. 82-83.
- Riley and Serres, p. 342.
- Ibid., p. 375.
- Ibid., p. 361.
- Ibid., p. 380.
- Stover, C.K., et al. "Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen," Nature, v. 406, p. 959.
* Frank Sherwin is a zoologist and seminar speaker with ICR.
Cite this article: Sherwin, F. 2001. Just How Simple Are Bacteria? Acts & Facts. 30 (2).









