A recently published study in the epigenetic modification of DNA regions similar among humans and three different apes not only provided a completely mixed up picture of evolution, but one that was entirely backwards.1
Epigenetic modifications are chemical tags that are added along chromosomes in specific patterns that control how genes are expressed. At present, 12 different types of gene regulating modifications (i.e., chemical tagging) to histone proteins that package the DNA molecule are well-documented in the human genome.2 In addition to the modification of histones, the DNA molecule itself can be tagged by methyl groups on the cytosine nucleotide bases. Thus, the combinatorial epigenetic code is exceedingly complex, but key to understanding how the genome works.
While the DNA code is closely similar in all cells throughout the human body, the epigenetic code and its patterns vary depending on cell and tissue type.2 Because these epigenetic patterns control how genes are expressed in the cell, evolutionists have been interested in comparing the patterns between humans and apes to check for commonalities and dissimilarities. Interestingly, a comparative epigenetic study just published by evolutionary scientists completely contradicts the standard, inferred evolutionary tree for human-ape evolution.
In this study, researchers examined the DNA methylation patterns in the blood cells of humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans.1 They focused on the areas of chromosomes 21 and 22 that are highly similar among all four human and ape genomes. The regions between the chromosomes that were too dissimilar (>98.8 percent identical) were not compared. Another recent study has shown that overall, chimp chromosomes 21 and 22 are on average 76.2 and 77.9 percent similar, respectively, in their actual DNA sequence compared to human.3 Thus, there are areas on these chromosomes that are very similar and other regions that are not. Comparative epigenetics, like many other types of evolutionary DNA studies, can only be done on the areas between chromosomes that are highly similar.
In the study, 16 different regions were identified that exhibited strong DNA methylation pattern differences between humans and chimps. These regions were then chosen for further comparison with gorillas and orangutans. The regions were also highly different between humans and the other apes, but not in the levels and patterns one might anticipate based on evolutionary predictions.
When the researchers used the DNA methylation data from the 16 different regions to form an evolutionary tree, it was completely backwards compared to the commonly believed order of evolution for apes that supposedly led up to humans. (See Figure below.) Orangutans, who supposedly are the least evolved among apes compared to humans, actually had more DNA methylation patterns similar to humans than chimps or gorillas. And if that was not enough, gorillas were the next closest in similarity to humans with chimps falling out last! According to evolutionary predictions, chimps should have been most similar to humans, then gorillas, and lastly orangutans.
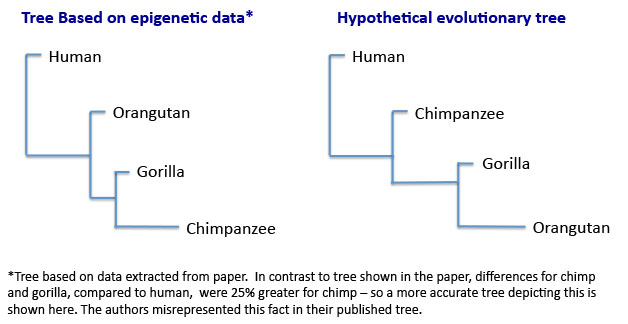
Major differences between human and chimp epigenetic profiles have been noted before.4 But these study results are particularly interesting because they utterly defy all predictions in the evolutionary paradigm—literally turning it on its head and showing that it is a fallible model of human origins.
These results continue to verify the biblical account of creation wherein all forms of life—including humans, chimps, gorillas, and orangutans—were each created after their kind, uniquely and independently.
References
- Fukuda, et al. 2013. Regional DNA methylation differences between humans and chimpanzees are associated with genetic changes, transcriptional divergence and disease genes. Journal of Human Genetics. 58 (7): 446–454.
- The ENCODE Project Consortium. 2012. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. 489 (7414): 57-74.
- Tomkins, J. 2013. Comprehensive Analysis of Chimpanzee and Human Chromosomes Reveals Average DNA Similarity of 70%. Answers Research Journal. 6 (1): 63–69.
- Tomkins, J. 2013. Epigenetics Proves Humans and Chimps Are Different. Acts & Facts. 42 (1): 11-12.
* Dr. Tomkins is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and received his Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University.
Article posted August 16, 2013.