Not just horses and fish, but—like a whole ancient zoo buried together—lizards, alligators, stingrays, snakes, squirrel varieties, bats, long-tailed turtles, lemur-like primates, birds, frogs, insects, and sycamore, palm, and fern leaves were all fossilized in Wyoming's Green River Formation. A new book showcasing some of the more spectacular fossils provides secularists another opportunity to reinforce their ideas about how these diverse creatures were encased in what became a giant rock formation. Commonsense observations refute their slow-and-gradual scenario, however, and point to a more violent explanation.
Lance Grande collected the stunning fossil images for the book, The Lost World of Fossil Lake: Snapshots from Deep Time. He works as one of the curators at Chicago's Field Museum of Natural History. One of his images shows a now-extinct variety of horse—one with a tiny stature and long hind legs for its size—surrounded by fossil fish. Horses and fish don't usually hang out together, but apparently they died together. How did they end up in the same fossilized bed?
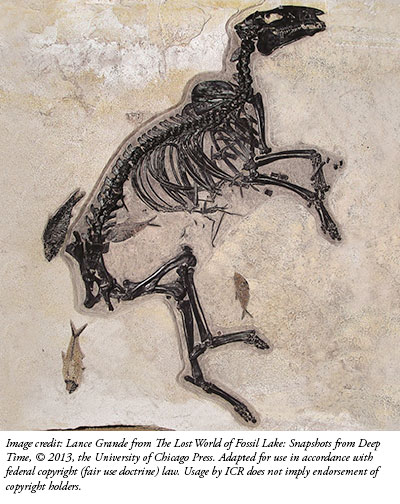 LiveScience featured some of the book's images on its website, including the "Mini-Horse." There, its image caption reads, "Researchers aren't sure how the horse ended up at the bottom of the middle of Fossil Lake but they suspect it drowned, possibly trying to escape a predator."1 Then, supposedly its carcass sank neatly to the bottom without having been scavenged by any of the many fish represented in the formation's fossils.
LiveScience featured some of the book's images on its website, including the "Mini-Horse." There, its image caption reads, "Researchers aren't sure how the horse ended up at the bottom of the middle of Fossil Lake but they suspect it drowned, possibly trying to escape a predator."1 Then, supposedly its carcass sank neatly to the bottom without having been scavenged by any of the many fish represented in the formation's fossils.
The horse body's next trick also defied commonsense. According to LiveScience, "Over thousands of years, dead animals rained down into the muck deep below the surface of long-gone Fossil Lake."2 Not only does the slow-and-gradual story require a magic wand to wave off the persistent problem of scavenging, but it calls upon the ancient deep "muck" to do what experiments have shown it cannot do—keep a carcass from rotting away to nothing.
And what strange process preserved these animal bodies so well as they supposedly rested on the lake bed before the slow-settling sediments covered and buried them over the long years? This story defies horse sense. Clearly, they had to have been buried deeply by fast-building sediment in order to preserve at such high quality.
Supposedly, a lack of oxygen preserved the whole carcasses. But God created microbes to function even without readily available oxygen. The problem is that fish and other animal carcasses rot in just a few weeks, even when buried in mud that has very little oxygen.3 What the scavengers don't eat, anoxic microbes quickly consume. That is why today's anoxic lake and ocean bottom muds form no fossils.
Whatever buried the horse did so rapidly and catastrophically. Fast-flowing water mixed with fresh volcanic ash and washed over the diverse assembly of creatures, burying them alive and trapping them in the Green River's series of basins.
The Genesis Flood provides a context for that catastrophe. Some creation geologists suggest that residual catastrophes immediately after the Flood formed Green River Formation, while others propose that it formed when water ran off the continents in the waning Flood months. Either scenario sets a catastrophic-enough stage to trump slow-and-gradual speculations and to bury alligators, horses, lizards, and fish together quickly and completely.
References
- Gannon, M. Images: Stingray Sex, Mini-Horses & Other Curiosities of Fossil Lake. LiveScience. Posted on LiveScience.com June 9, 2013, accessed June 10, 2013.
- Gannon, M. Lost World Locked in Stone at Fossil Lake. LiveScience. Posted on LiveScience.com June 9, 2013, accessed June 10, 2013.
- Donovan, S.K., (Ed.) 1991. The Process of fossilization. New York: Columbia University Press, 120-129.
Image credit: Lance Grande from The Lost World of Fossil Lake: Snapshots from Deep Time, © 2013, the University of Chicago Press. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on June 17, 2013.