Exciting research from the summer of 2012 described DNA variation in the protein coding regions of the human genome linked to population growth. One of the investigation's conclusions was that the human genome began to rapidly diversify not more than 5,000 years ago.1,2 This observation closely agrees with a biblical timeline of post-flood human diversification. Yet another study, this one published in the journal Nature, accessed even more extensive data and unintentionally confirmed the recent human history described in Genesis.3
Differences in human DNA can be characterized across populations and ethnic groups using a variety of techniques. One of the most informative genetic technologies in this regard is the analysis of rare DNA variation in the protein coding regions of the genome. Variability in these regions is less frequent than the more numerous genetic differences that occur in the non-coding regulatory regions. Researchers can statistically combine this information with demographic data derived from population growth across the world to generate time scales related to human genetic diversification.4
What makes this type of research unique is that evolutionary scientists typically incorporate hypothetical deep time scales taken from the authority of paleontologists or other similar deep-time scenarios to calibrate models of genetic change over time. Demographics-based studies using observed world population dynamics do not rely on this bias and are therefore more accurate and realistic.
In a 2012 Science report, geneticists analyzed DNA sequences of 15,585 protein-coding gene regions in the human genome for 1,351 European Americans and 1,088 African Americans for rare DNA variation.1,2 This new study accessed rare coding variation in 15,336 genes from over 6,500 humans—almost three times the amount of data compared to the first study.3 A separate group of researchers performed the new study.
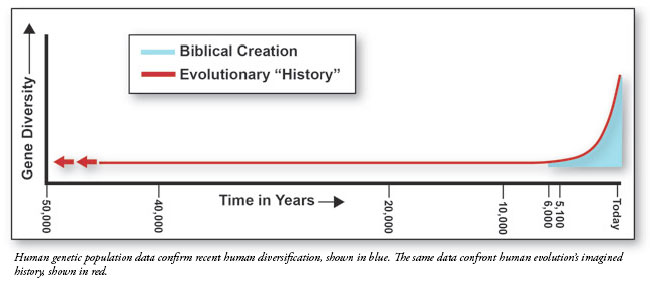
The Nature results convey a second spectacular confirmation of the amazingly biblical conclusions from the first study. These scientists confirmed that the human genome began to rapidly diversify not more than 5,000 years ago. In addition, they found significant levels of variation to be associated with degradation of the human genome, not forward evolutionary progress. This fits closely with research performed by Cornell University geneticist John Sanford who demonstrated through biologically realistic population genetic modeling that genomes actually devolve over time in a process called genetic entropy.5
According to the Bible, the pre-flood world population was reduced to Noah's three sons and their wives, creating a genetic bottleneck from which all humans descended. Immediately following the global flood event, we would expect to see a rapid diversification continuing up to the present. According to Scripture, this began not more than 5,000 years ago. We would also expect the human genome to devolve or degrade as it accumulates irreversible genetic errors over time. Now, two secular research papers confirm these biblical predictions.
References
- Tomkins, J. 2012. Human DNA Variation Linked to Biblical Event Timeline. Creation Science Update. Posted on icr.org July 23, 2012, accessed December 31, 2012.
- Tennessen, J. et al. 2012. Evolution and Functional Impact of Rare Coding Variation from Deep Sequencing of Human Exomes. Science. 337 (6090): 64-69.
- Fu, W, et al. Analysis of 6,515 exomes reveals the recent origin of most human protein-coding variants. Nature. Published online before print, July 13, 2012.
- Keinan, A and A. Clark. 2012. Recent Explosive Human Population Growth Has Resulted in an Excess of Rare Genetic Variants. Science. 336 (6082): 740-743.
- Sanford, J. C. 2008. Genetic Entropy and the Mystery of the Genome, 3rd ed. Waterloo, NY: FMS Publications.
* Dr. Tomkins is a Research Associate and received his Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University.
Article posted on January 9, 2013.