Nineteenth-century English poet Alfred Tennyson famously described nature as "red in tooth and claw."1 But were claws and teeth originally intended to draw blood, or were they used to eat vegetation?
Recently, three U.S. biologists studied the feeding habits of 11 Central and South American leaf-nosed bats and looked for "relationships between diet, tooth structure, feeding performance, and behaviour."2 Some bats eat insects and small vertebrates, some eat fruit and nectar, others a little bit of everything. Vampire bats, of course, will eat blood.
To conduct their research, which was published in 2011, the team generated three-dimensional images of the teeth and skulls of 17 bat species. The BBC featured some of the images on its website, such as the fruit bat skull below.3
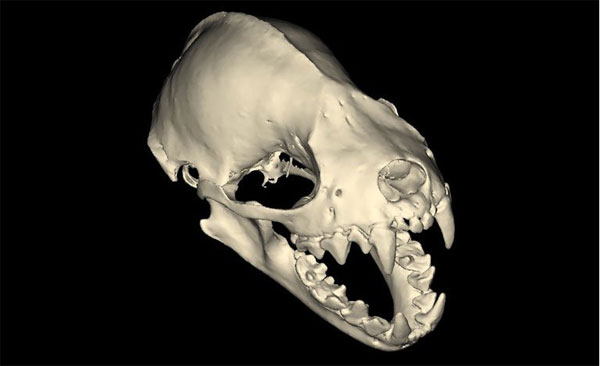
The study authors found that fruit bats have more complicated surface features on their molars, which they use to crush fruit pulp. Insectivorous bat molars have pointed crests that are more efficient at shearing insect exoskeletons.
A 2012 study of multiple large fruit bat species that inhabit the same locations in Brazil found that although their chromosomes looked virtually indistinguishable at first, species-specific banding patterns show up when stained.4 A separate 2011 study found "a considerable range of individual variation" in Phyllostomatid vampire bat skulls.5
Since bat features are still adapting today, it stands to reason that the original Phyllostomatid bats that colonized the Americas also adapted their features as they diversified into today's species. But no evidence suggests either that bats evolved from non-bats or that they will ever evolve into a non-bat.
The fact that fruit bats use their sharp teeth to eat fruit fits with the biblical teaching that God originally intended animals to eat vegetation, not other animals:
Large, sharp teeth are not used solely for killing and ripping flesh from other animals. Fruit bats have sharp, pointed teeth, similar to those in cats, designed to quickly tear flesh from fruit. These teeth easily could remove flesh from an animal, but the fruit bat does not use them for this purpose.6
And the fact that other bats eat blood fits with the biblical teaching that sin resulted in a cursed creation. Bats now use their vegetation-eating equipment with less discrimination.
It makes sense that God would supply various creatures with large, sharp teeth so that they could eat the varied plant products He provided for their nourishment.7 But since the "law of sin and death" now operates in this world, animals and humans use what was originally good to accomplish what is inherently not good.8
References
- Tennyson, A. 1849. In Memoriam A. H. H., Canto 56.
- Santana, S. E., S. Strait, and E. R. Dumont. 2011. The better to eat you with: functional correlates of tooth structure in bats. Functional Ecology. 25 (4): 839-847.
- Sharp teeth aid bats' fruit diets. BBC Earth News. Posted on news.bbc.co.uk February 25, 2011, accessed February 25, 2012.
- de Lemos Pinto, M. et al. 2012. Cytotaxonomy of the subgenus Artibeus (Phyllostomidae, Chiroptera) by characterization of species-specific markers. Comparative Cytogenetics. 6 (1): 17-28.
- Orihuela, J. 2011. Skull variation of the vampire bat Desmodus rotundus (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae): Taxonomic implications for the Cuban fossil vampire bat Desmodus puntajudensis. Chiroptera Neotropical. 17 (1): 863-876.
- Criswell, D. 2009. Predation Did Not Come from Evolution. Acts & Facts. 38 (3): 9.
- Genesis 1:30.
- Romans 8:2.
Skull image credit: Dumont Lab, University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on March 26, 2012.














