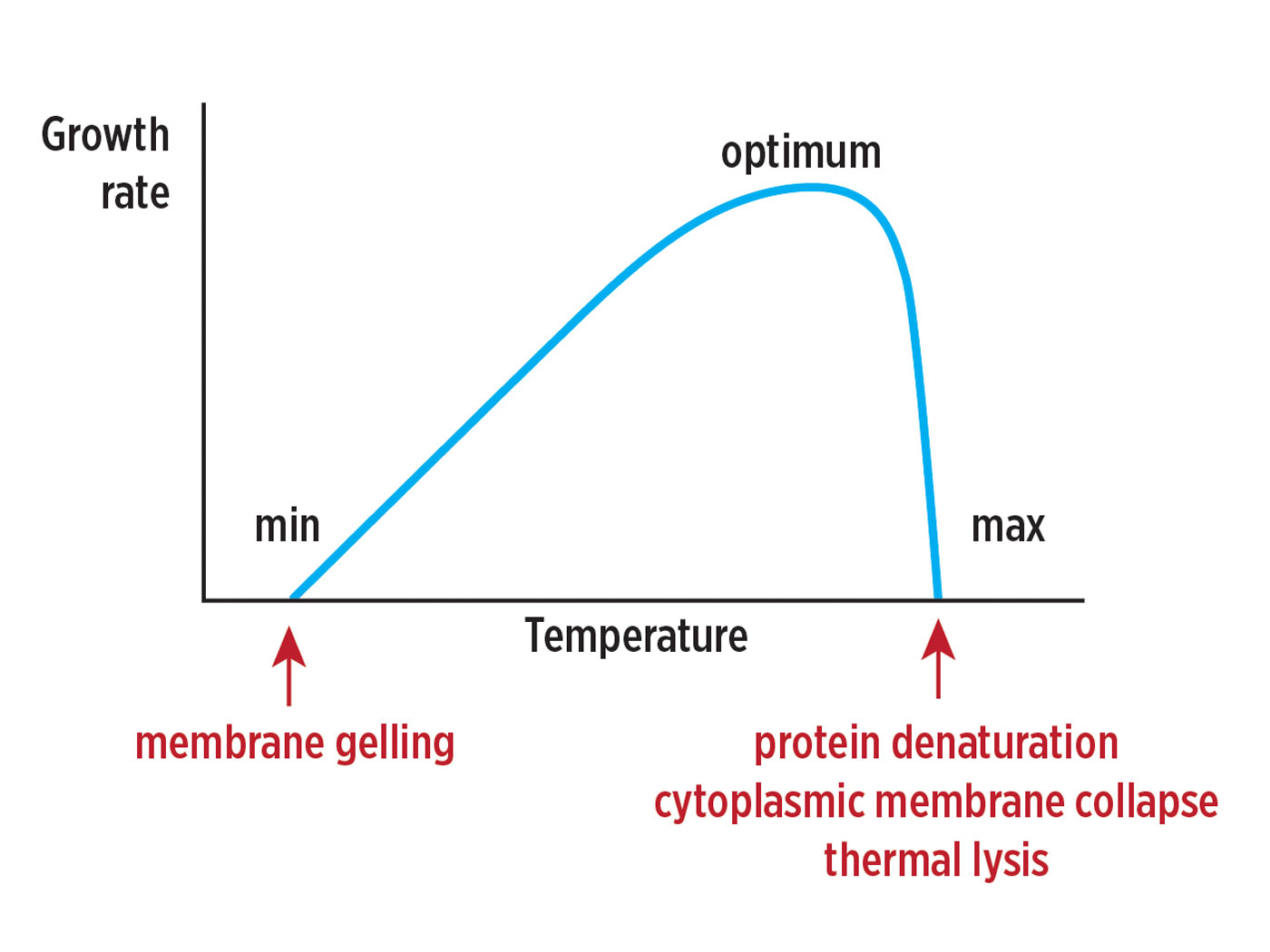
The concept of natural selection remains controversial in both the evolutionary and creationist communities. Classical evolutionists still cannot clearly define it as they continue to debate one another over a valid model and definition. Meanwhile, secular molecular biologists are content to leave the debate primarily in the hands of the classical biologists when the hard data needed to validate natural selection in one form or another ultimately lies at the molecular level. This is typical of the compartmentalized nature of modern academics where scientists focus on a single area of specialty research and assume that some other sector of biology will solve the serious problems of Darwinian evolution.
The lack of a clearly defined molecular mechanism to create new irreducibly complex traits as a creative force in evolution is why many scientists have had difficulty characterizing Darwin’s concept for over 70 years. Dr. Randy Guliuzza recently pointed out the various key philosophical and semantic anomalies of the confusing quagmire surrounding the usage of natural selection terminology.1 Dr. Guliuzza not only exposed the various obfuscated semantics involved, but he also fully substantiated his deductions by quoting the evolutionists in their own words.2
The next and perhaps most important step following Dr. Guliuzza’s effort is for the ICR biological sciences team to begin illustrating the many interesting cellular mechanisms that allow organisms to adapt to new environments or changes in their existing environments. To some extent, this has already been going on through ICR biologist Brian Thomas’ daily news articles and other ICR bio-scientists’ publications in various journals and in Acts & Facts.
Most expressed traits and adaptations are biologically complex responses. These adaptations can be defined as biological interactions at the environmental interface that are regulated by genetic programming and cell physiology. A creationist model of adaptation is based on an organism’s innate physiological capabilities and fault tolerance mechanisms that are genetically programmed by the Creator. Scientifically valid descriptions of adaptation employ recent molecular discoveries in genomics, cell physiology, and phenotypic plasticity to explain how living creatures successfully interface with environmental challenges and fill ecological niches.
Environmental stresses and stimuli cannot exercise the creative causation of highly complex pre-coded genetic information that underlies irreducibly complex systems of adaptation. Organismal interaction with the environment involves highly complex and dynamic physiological and genetic responses to a wide range of physical and chemical sensory cues. These environmental cues are perceived by complex systems of cell sensor networks that interact with an organism’s highly engineered genetic system. While adaptation systems are complex and flexible, they are not evolvable on a grand neo-Darwinian scale. They are pre-engineered, pre-programmed, and irreducibly complex in the strictest sense of the term, and they unequivocally imply the infinite intelligence of our Creator God.
An upcoming research column will discuss the concept of genetic diversity in biological adaptation. For a review of genetic diversity at an introductory level, see the recent ICR publication by Parker and Tomkins.3
References
- See Guliuzza, R.J. 2012. Darwin’s Sacred Imposter: Answering Questions about the Fallacy of Natural Selection. Acts & Facts. 41 (2): 12-15.
- Guliuzza, R. 2011. Darwin’s Sacred Imposter: Recognizing Missed Warning Signs. Acts & Facts. 40 (5): 12-15; Guliuzza, R. 2011. Darwin’s Sacred Imposter: How Natural Selection Is Given Credit for Design in Nature. Acts & Facts. 40 (7): 12-15; Guliuzza, R. 2011. Darwin’s Sacred Imposter: The Illusion That Natural Selection Operates on Organisms. Acts & Facts. 40 (9): 12-15; Guliuzza, R. 2011. Darwin’s Sacred Imposter: Natural Selection’s Idolatrous Trap. Acts & Facts. 40 (11): 12-15.
- Parker, G. and J. Tomkins. 2010. Genetic Diversity. Dallas, TX: Institute for Creation Research.
* Dr. Tomkins is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and received his Ph.D. in Genetics from Clemson University.
Cite this article: Tomkins, J. 2012. Mechanisms of Adaptation in Biology: Molecular Cell Biology. Acts & Facts. 41 (4): 6.