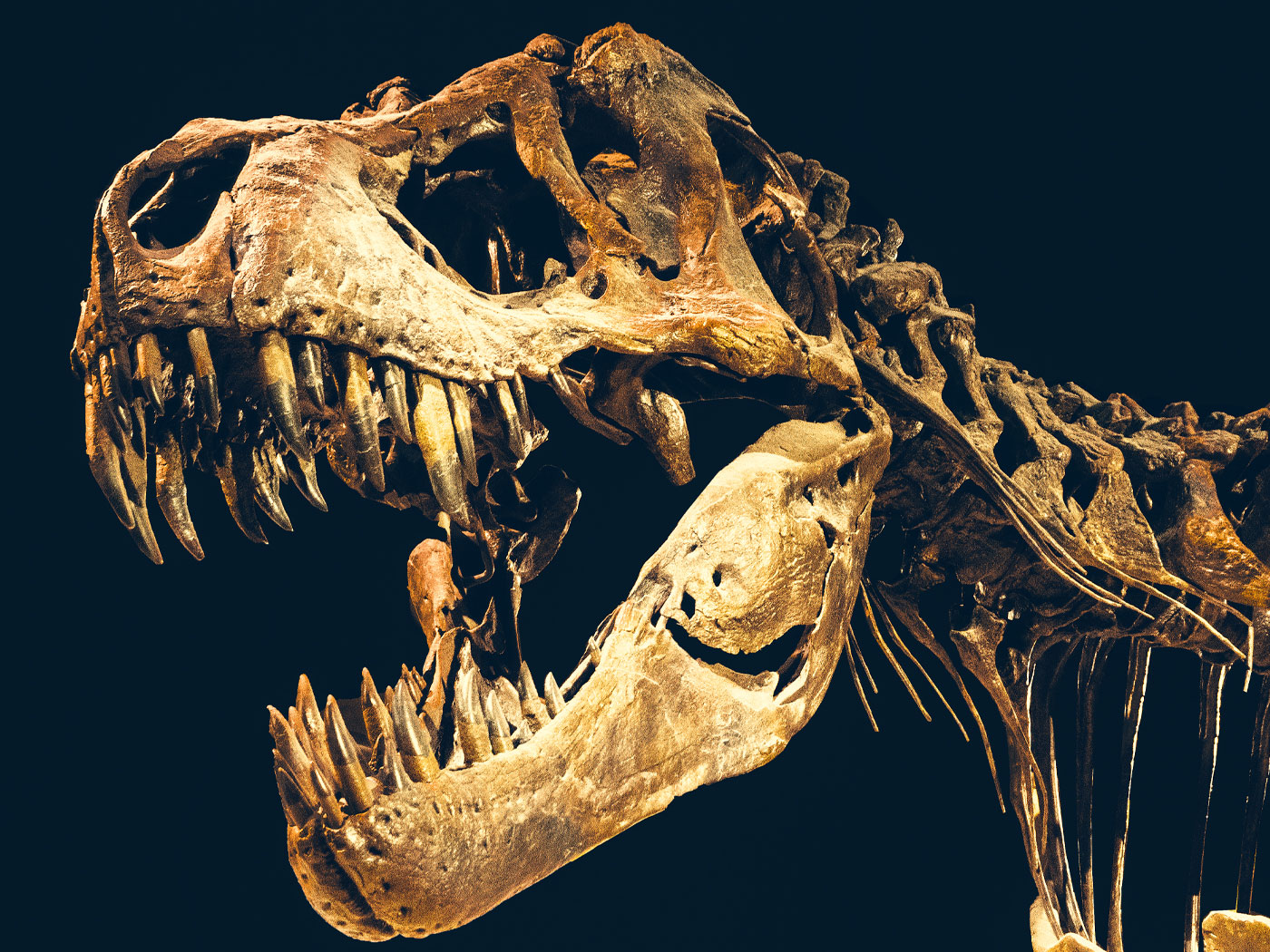
The most popular dinosaur is probably Tyrannosaurus rex, a Latin term that loosely translates as “king lizard.” Based on evolutionary assumptions, scientists have long held that these dinosaurs lived for “only” 3 million years, approximately 68 to 65 million years ago. A fossil looking remarkably like a small version of T. rex, however, has been located in a much lower rock layer.1 Using the evolutionary dates assigned to the relevant strata, this adds 60 million years to the T. rex timeline. If the evolutionary interpretation was this wrong about one creature, can it be trusted on the rest of the fossil record?
Nicknamed Raptorex, this comparatively small dinosaur shared with T. rex “a proportionately large skull, incisiform premaxillary teeth, expanded jaw-closing musculature, diminutive forelimb, and a hindlimb with cursorial proportions,” according to a report recently published in Science.1
The Lower Cretaceous rocks that Raptorex was found in have been assigned a date of approximately 125 million years. But that would mean that this mini-T. rex was unaware that its body plan was not supposed to have evolved for another 60 million years. Paleontologist and report co-author Stephen Brusatte admitted fossils like this “totally throw us for a curve” and are “completely unexpected.”2 A similar find was made recently in Japan of teeth from a mid-sized T. rex discovered in rock dated at 140 million years.3
Because of finds like these, evolutionary history must accommodate tyrannosauroids (dinosaurs sharing the same core features as the T. rex) having evolved suddenly 140 million years ago, living virtually unchanged in form for 65 million years, then going extinct for an unknown reason. But with such an unimaginably long time for mutations to have been selected, how was it possible for these creatures to have remained so similar if the evolutionary scenario is correct?4
If the vast majority of tyrannosauroid fossils were deposited during the one-year Flood of Noah, however, when “all flesh died that moved upon the earth,”5 then it would stand to reason that their remains—preserved across extensive vertical strata—together represent a snapshot of animals that existed at that time but in different habitats, rather than a record of creatures that died over eons. The distribution of marine fossils in lower layers and terrestrial forms higher up corresponds not to long ages of evolution, but to successive waves or stages of the Flood as the waters encroached higher and higher until the land was totally inundated.
The biblical historical framework offers no reason why the rock layer that this new tyrannosauroid was found in, or that of the Japanese T. rex teeth, should be “completely unexpected.” On the contrary, it fits perfectly with the Genesis record of the Flood.
References
- Sereno, P. C. et al. 2009. Tyrannosaurid Skeletal Design First Evolved at Small Body Size. Science. Published online September 17, 2009, accessed September 18, 2009.
- Ansari, A. Tiny T rex fossil discovery startles scientists. CNN. Posted on cnn.com September 17, 2009, accessed September 18, 2009.
- Thomas, B. 2009. T. Rex Teeth Take a Bite Out of Evolution. ICR News. Posted on icr.org July 17, 2009, accessed September 18, 2009.
- The same problem for evolution is distinct in the case of tuataras. See Thomas, B. 2009. Why Are There Still Tuataras? ICR News. Posted on icr.org August 12, 2009, accessed September 18, 2009.
- Genesis 7:21.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on September 29, 2009.