Brain researchers from San Diego State University have just reported digitally capturing the dense folds of a preserved human cerebellum using a high resolution MRI device.1 Once thought to merely coordinate rote body movements, these brain folds contain newly revealed design features that challenge conventional concepts of where the human brain came from.
The cerebellum, which literally in Latin means “tiny brain,” lies nearer the center of our heads, beneath the larger cerebral cortex. Sheets of nervous tissue fold hundreds of times within a cerebellum, but how big are those sheets? The SDSU team has designed software to digitally unfold the MRI-scanned tissue layers.2
Their new map shows that the tissue comprising the human cerebellum would unfurl into two sheets, each three-feet long and four inches wide. Its total surface area makes up a whopping 78 percent of the larger cerebral cortex. In other words, the cerebellum has many more folds than the cerebral cortex. What’s more, the team found that those folds cross one another in patterns unique to humans. They published their results in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).1
The study authors also scanned and digitally unfolded a macaque (monkey) cerebellum for comparison to the human one. They found fewer folds and fewer cross-touching folds in the monkey brain. Plus, the macaque cerebellum makes up only about 30 percent of its own cerebral cortex.
What function do the uniquely large and uniquely folded membranes serve in humans as opposed to primates?
Patches of nervous tissue within the cerebellum connect with various body parts. Lead author and brain expert Martin Sereno described this connection to SDSU NewsCenter saying, “You get a little chunk of the lip, next to a chunk of the shoulder or face, like jumbled puzzle pieces.” The significance, according to Sereno, is that, “when you think of the cognition required to write a scientific paper or explain a concept, you have to pull in information from many different sources. And that’s just how the cerebellum is set up.”2
So, the cerebellum “is set up” (not jumbled) specifically to enable people (not primates) to think abstractly and logically. Using similar words in their PNAS report, the team wrote, “The peculiar cerebellar style of computation, in which small internally organized patches from distant sources are brought together like a jumbled picture puzzle, might be able to help with higher-level computations, such as those involved in language or abstract reasoning.”1 Thus, our uniquely human attributes of computing, language, and reasoning quite likely require the precise and intricate fold patterns unique to the human cerebellum.
How did these “internally organized patches” get organized? In the real world, organization—the coordination of various parts to fit and function for a purpose—always happens on purpose. However, the SDSU team credited evolution with this innovation.3 In typical fashion, they offered no evidence that any of evolution’s natural processes could or would organize brain matter into complicated functional folds.
Crediting an actual being like a Creator more realistically explains the brilliance, foresight, and technical expertise obviously required to organize the human cerebellum and integrate it with human body function.
References
1. Martin I. Sereno et al., “The human cerebellum has almost 80% of the surface area of the neocortex,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117, no. 32 (July 28, 2020): 19538-19543, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002896117.
2. Nagappan, P. ‘Little Brain’ or Cerebellum Not So Little After All. San Diego State University NewsCenter. Posted on Newscenter.sdsu.edu July 31, 2020, accessed August 4, 2020.
3. Sereno told SDSU NewsCenter, “The fact that it has such a large surface area speaks to the evolution of distinctively human behaviors and cognition. It has expanded so much that the folding patterns are very complex.” See Nagappan, P. ‘Little Brain’ or Cerebellum Not So Little After All. San Diego State University NewsCenter. Posted on Newscenter.sdsu.edu July 31, 2020, accessed August 4, 2020.
*Dr. Brian Thomas is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool.
Human Brain Research Finds New Folds
The Latest
Honoring Our Leaders
"Obey them that have the rule over you, and submit yourselves: for they watch for your souls, as they that must give account, that they may do...
Dismissals and Fiction: A Review of Hugh Ross’ Book Noah’s...
Hugh Ross’ latest book, Noah’s Flood Revisited: New Depths of Insight from Science and Scripture, is both dismissive of young earth creation...
Secrets of Pre-Flood Ecosystems and Atmosphere Revealed
What was the pre-Flood world like thousands of years ago?1,2 With the advent of unearthing soft tissues in fossils,3 creation...
Confirmed New Record for Most Distant Galaxy
A galaxy with the designation MoM-z14 has recently been confirmed as the most distant galaxy ever detected.1,2 By Big Bang reckoning, we...
Insect Eyes Reflect Creation
Research into insect eyes continues to reveal amazing structure and function. For example, although fruit flies’ eyes are attached firmly to their...
February 2026 ICR Wallpaper
"Be strong and of good courage, do not fear nor be afraid of them; for the LORD you God, He is the One who goes with you. He will not leave you...
Microgravity's Effect on Bacteriophages Is Not Evolution
The word evolution is often used imprecisely, leading the public to believe that any biological change is evolution, and, therefore, it’s a fact.1...
Engineered for Extremes: The Hidden Precision of a Salt Lake...
Water that is nearly five times saltier than the ocean is deadly to most animals. But in Utah’s Great Salt Lake, scientists have found a tiny...
CREATION PODCAST
Giant Sequoias: Too Complex to Be Accidental | The Creation Podcast:...
What living thing grows taller than a 25-story building, survives raging wildfires, and actually depends on those fires to reproduce? Giant sequoias...
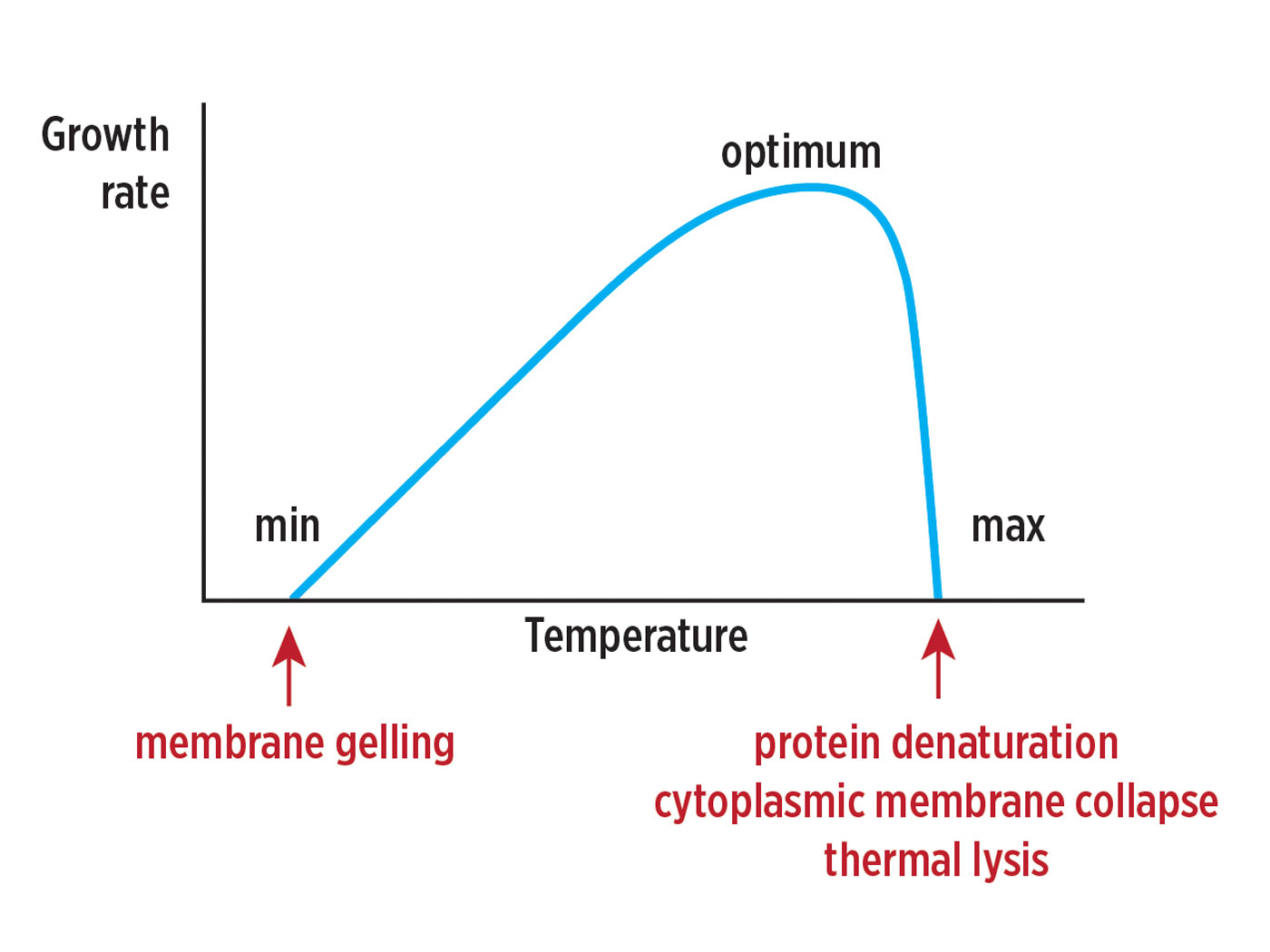
Bound by Design: How a Universal Temperature Law Reveals Life’s...
What if every living creature—from coral reefs and cold-water fish to mountain flowers and desert reptiles—followed the same hidden temperature...