 Butterflies and moths fluttering around a flower are a beautiful sight. They innocently lap up nectar and float on the wind. Countless plants depend on the pollination that occurs during their feeding.
Butterflies and moths fluttering around a flower are a beautiful sight. They innocently lap up nectar and float on the wind. Countless plants depend on the pollination that occurs during their feeding.
One group of moths, however, deviates from this utopian state by feeding on blood. Meet the vampire moth.1,2 Like a tiny flying Dracula, this moth creeps up on its sleeping prey and drills into its skin with a ferocious tooth- and claw-covered proboscis. Inflatable hooks on the tip of the feeding tube firmly anchor it to the skin while it feasts on the prey’s blood.
Was the vampire moth designed to be a blood-feeder? The electron microscope image of the Calyptra moth’s mouthparts in Figure 1 shows that the tip is reinforced for piercing and the sides are laced with tearing hooks, rasping spines, and erectile barbs. The teeth rip away at blood vessels, causing a pool of blood to form under the skin for the moth to drink.
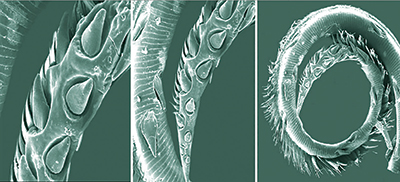
Vampire moths feed on humans, zebu, cattle, rhinoceros, and even elephants. These moths seem purposely built with all the tools they need to drink blood, right? Well, the truth may surprise you. What was the Calyptra moth actually built to do? Eat fruit.4
Nearly all 150 or so moth species in the Calpini tribe feed exclusively on fruit. Only about 10 species have been definitively identified as blood-feeders. Because the majority of Calpini moths never taste blood, we can conclude that the tearing hooks and spines are designed to make what is, essentially, a fruit smoothie. The inflatable hooks expand to make a larger pool of fruit juice to drink. The moths feed on oranges, grapefruit, strawberries, raspberries, cherries, and even tough-skinned longan and litchi.
The vampire moth’s mouthparts look threatening—but so do the blades of a store-bought blender. What if the moth had been named “the fruit smoothie moth” and all anyone knew about were its fruit-eating habits? Maybe then you could reason that the purpose of the menacing-looking hooks in Figure 1 is to juice the inside of a raspberry. If you later discover that the moth can also use them to “bite” and drink blood, you would recognize this wasn’t necessarily their original intention. Learning about the feeding habits in this order doesn’t naturally lead to the incorrect conclusion that God designed moths to suck blood.
Butterflies and moths may feed on carrion, dung, wounds, tears, and sweat in the absence of their primary food source. Evolution bombards us with the message that death is normal,5 and that can influence us to think that sharp teeth or claws were made to snack on blood or flesh.
But there are no differences in the equipment of fruit-feeding and blood-feeding moths.3 Moths use tools originally designed for a good purpose in a now-harmful way when fruit is unavailable. Like other predators living today, God originally designed them for the vegetarian diet all creatures had in the beginning.6
References
- Plotkin, D. and J. Goddard. 2013. Blood, sweat, and tears: a review of the hematophagous, sudophagous, and lachryphagous Lepidoptera. Journal of Vector Ecology. 38 (2): 289-294.
- Zaspel, J. M. et al. 2014. Geographic Distribution, Phylogeny, and Genetic Diversity of the Fruit- and Blood-Feeding Moth Calyptra thalictra Borkhausen (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Journal of Parasitology. 100 (5): 583-591.
- Zaspel, J. M., S. J. Weller, and M. A. Branham. 2011. A comparative survey of proboscis morphology and associated structures in fruit-piercing, tear-feeding, and blood-feeding moths in Calpinae (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Zoomorphology. 130 (3): 203-225.
- Zaspel, J. M. et al. 2016. Host-Related Olfactory Behavior in a Fruit-Piercing Moth (Lepidoptera: Erebidae) in Far Eastern Russia. Journal of Insect Science. 16 (1): 51.
- Guliuzza, R. J. 2020. Survival of the Fittest and Evolution’s Death Culture. Acts & Facts. 49 (1): 17-19.
- Genesis 1:29-30. See Criswell, D. 2009. Predation Did Not Come from Evolution. Acts & Facts. 38 (3): 9.
* Mr. Arledge is Research Coordinator at the Institute for Creation Research.
















